Clearwater: A Comprehensive Exploration of Clarity and Purity
Related Articles: Clearwater: A Comprehensive Exploration of Clarity and Purity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Clearwater: A Comprehensive Exploration of Clarity and Purity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Clearwater: A Comprehensive Exploration of Clarity and Purity
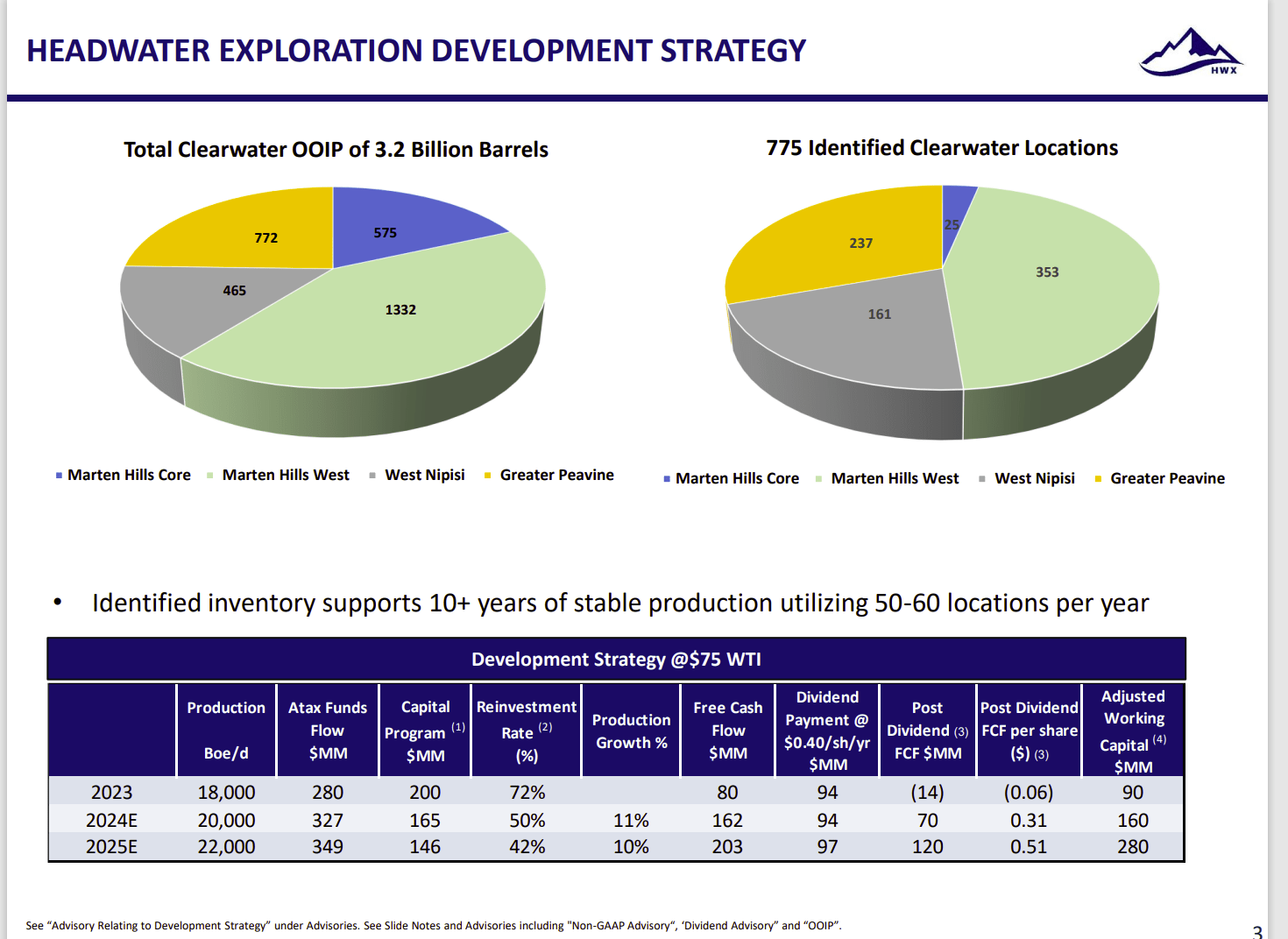
Clearwater is a term that encompasses a wide range of concepts and applications, each with its own unique significance. It can refer to the physical clarity of water, the absence of impurities, or the metaphorical clarity of thought and understanding. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of clearwater, examining its importance in various contexts, exploring its benefits, and addressing common questions and concerns.
I. The Physical Clarity of Water
Clearwater in its most literal sense refers to water that is free from visible impurities, such as suspended particles, sediment, or dissolved substances. This clarity is often associated with pristine natural environments, like crystal-clear lakes, rivers, and oceans. However, achieving clearwater in various applications requires careful management and treatment.
1.1. Importance of Clearwater in Ecosystems
The clarity of water plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems. Sunlight penetration is essential for photosynthesis by aquatic plants, which form the base of the food chain. Suspended particles can block sunlight, hindering plant growth and impacting the overall health of the ecosystem.
1.2. Clearwater in Drinking Water
Clearwater is fundamental for human health. Drinking water must be free from visible impurities and harmful contaminants to ensure its safety. Water treatment processes aim to achieve clearwater by removing suspended particles, bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants.
1.3. Clearwater in Industry
Many industries rely on clearwater for various processes. Manufacturing, agriculture, and power generation all require water that is free from impurities to prevent equipment damage, contamination, and operational disruptions.
II. The Purity of Water
Beyond physical clarity, clearwater also signifies the absence of harmful contaminants, both visible and invisible. This purity is essential for various applications, including drinking water, industrial processes, and environmental protection.
2.1. Contaminants and Their Impact
Water can be contaminated by various sources, including industrial waste, agricultural runoff, sewage, and natural processes. These contaminants can include bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, pesticides, and other harmful substances.
2.2. Water Treatment Technologies
To achieve clearwater purity, various water treatment technologies are employed. These include filtration, disinfection, coagulation, and other methods that remove or neutralize contaminants.
2.3. Importance of Water Quality Monitoring
Regular monitoring of water quality is crucial to ensure clearwater purity. This involves testing for specific contaminants, evaluating the effectiveness of treatment processes, and identifying potential sources of contamination.
III. The Metaphorical Clarity of Thought
Clearwater is often used metaphorically to represent clarity of thought, understanding, and perception. It signifies a state of mental clarity, free from confusion, ambiguity, or distractions.
3.1. Clarity in Communication
Clearwater in communication refers to the ability to express thoughts and ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding ambiguity and misunderstandings. This clarity is essential for effective communication in all aspects of life.
3.2. Clarity in Decision-Making
Clearwater in decision-making involves a clear understanding of the situation, the available options, and the potential consequences of each choice. This clarity allows for informed and rational decisions.
3.3. Clarity in Problem-Solving
Clearwater in problem-solving involves a clear identification of the problem, its root causes, and potential solutions. This clarity enables effective and efficient problem-solving.
IV. Related Searches and FAQs
4.1. Related Searches
- Water Treatment: This broad category encompasses various technologies and processes used to purify and treat water.
- Water Quality: This refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water, which determine its suitability for different uses.
- Water Contamination: This involves the introduction of harmful substances into water sources, posing risks to human health and the environment.
- Drinking Water Safety: This focuses on ensuring the safety of drinking water, including regulations, treatment processes, and monitoring.
- Environmental Protection: This encompasses efforts to protect and preserve water resources from pollution and degradation.
- Sustainable Water Management: This aims to manage water resources efficiently and sustainably, ensuring their availability for present and future generations.
- Water Conservation: This involves reducing water consumption through various measures, such as efficient appliances, water-saving techniques, and responsible water use practices.
- Water Scarcity: This refers to the lack of sufficient water resources to meet the needs of a population or region.
4.2. FAQs
- What are the main sources of water contamination?
- How is drinking water treated to ensure its safety?
- What are the signs of contaminated water?
- What are the health risks associated with contaminated water?
- How can I conserve water at home?
- What can I do to protect water resources?
- What are the challenges of water management in a changing climate?
- What are the latest advancements in water treatment technology?
V. Tips for Achieving Clearwater
- Reduce water consumption: Implement water-saving measures at home and work, such as low-flow showerheads, efficient appliances, and mindful watering practices.
- Properly dispose of chemicals and hazardous materials: Avoid dumping chemicals, pesticides, and other hazardous substances down the drain or into the environment.
- Support sustainable water management practices: Advocate for policies and initiatives that promote responsible water use and protect water resources.
- Educate yourself about water quality issues: Stay informed about local water quality concerns and advocate for clean water policies.
- Participate in water conservation programs: Join local initiatives and programs aimed at reducing water consumption and protecting water resources.
- Choose eco-friendly products: Opt for products that are manufactured with minimal environmental impact and do not contain harmful chemicals.
- Support organizations dedicated to clean water: Contribute to organizations working to provide clean water access and protect water resources worldwide.
VI. Conclusion
Clearwater is a concept with profound significance, encompassing both physical clarity and purity of water, as well as metaphorical clarity of thought and understanding. Achieving and maintaining clearwater in all its aspects is crucial for human health, environmental sustainability, and social progress. By understanding the importance of clearwater, employing responsible practices, and supporting initiatives that promote clean water access and conservation, we can ensure a future where clearwater is a reality for all.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Clearwater: A Comprehensive Exploration of Clarity and Purity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
