Landfall: Where the Storm Meets the Shore
Related Articles: Landfall: Where the Storm Meets the Shore
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Landfall: Where the Storm Meets the Shore. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Landfall: Where the Storm Meets the Shore

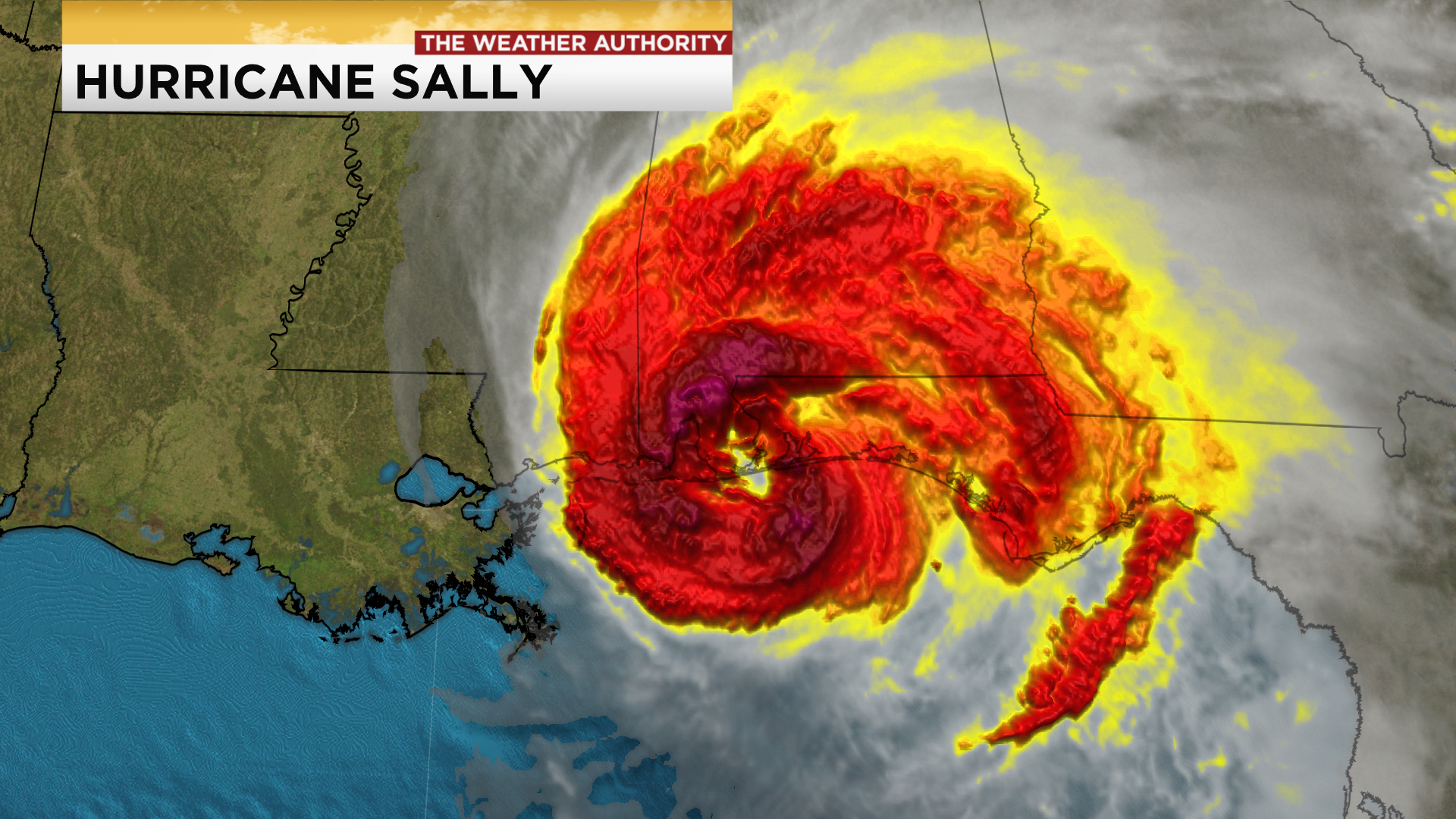
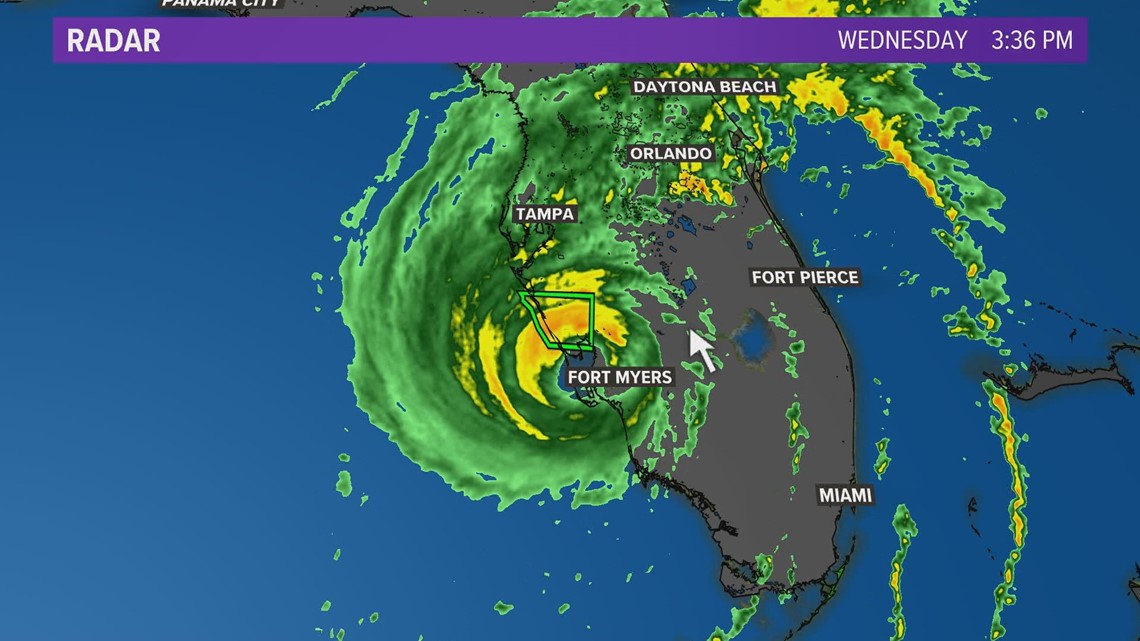
Landfall is a pivotal moment in the life cycle of a tropical cyclone, marking the transition from a purely oceanic phenomenon to a destructive force impacting land. It signifies the moment a storm’s center, or eye, makes contact with a coastline, bringing with it the full force of its winds, heavy rainfall, and potentially devastating storm surge. While the term landfall is most commonly associated with hurricanes, it can also be used to describe the arrival of any tropical cyclone, including typhoons and cyclones, on land.
Understanding the Impact of Landfall
The impact of landfall is multifaceted and can vary significantly depending on the intensity of the storm, the geographic location, and the preparedness of the affected area. Here’s a breakdown of the primary effects:
1. High Winds:
- Wind Speed and Damage: The strength of a storm’s winds is measured using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, ranging from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (over 157 mph). Higher wind speeds result in more significant damage, including downed trees, power outages, structural damage to buildings, and flying debris.
- Coastal Erosion: High winds can generate powerful waves that erode coastlines, causing beach loss, damage to coastal infrastructure, and flooding.
- Impact on Transportation: Strong winds can disrupt transportation systems, grounding airplanes, closing bridges and roads, and hindering emergency response efforts.
2. Heavy Rainfall:
- Flooding: Intense rainfall can lead to widespread flooding, particularly in areas with poor drainage systems. This can inundate homes, businesses, and infrastructure, causing significant damage and displacement.
- Landslides: Heavy rainfall can saturate soil, increasing the risk of landslides, especially in mountainous regions. This can block roads, damage property, and pose a threat to life.
- Waterborne Diseases: Stagnant floodwaters can become breeding grounds for disease-carrying mosquitoes and other insects, increasing the risk of waterborne illnesses like dengue fever, malaria, and typhoid.
3. Storm Surge:
- Sea Level Rise: Storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s strong winds pushing water towards the shore. This can result in significant coastal flooding, even in areas not directly hit by the eye of the storm.
- Coastal Inundation: Storm surge can inundate low-lying coastal areas, damaging homes, businesses, and infrastructure. It can also cause saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources, contaminating drinking water.
- Damage to Coastal Ecosystems: Storm surge can disrupt coastal ecosystems, damaging mangroves, coral reefs, and other marine habitats.
4. Social and Economic Impacts:
- Disruption of Daily Life: Landfall can disrupt daily life, forcing residents to evacuate, leading to school closures, business interruptions, and disruptions to transportation and communication.
- Power Outages: High winds and flooding can damage power lines, resulting in widespread power outages that can last for days or even weeks.
- Economic Losses: Landfall can cause significant economic losses, including property damage, business closures, and disruptions to supply chains.
- Humanitarian Crisis: In extreme cases, landfall can result in a humanitarian crisis, requiring extensive relief efforts to provide food, water, shelter, and medical care to affected populations.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Landfall:
- Hurricane Track: The path a hurricane takes is referred to as its track. Predicting a hurricane’s track is crucial for issuing accurate warnings and preparing for landfall.
- Hurricane Intensity: Hurricane intensity refers to the strength of a hurricane, measured using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. Predicting a hurricane’s intensity is essential for determining the potential impact of landfall.
- Hurricane Forecasting: Hurricane forecasting involves using sophisticated models and data analysis to predict a hurricane’s path, intensity, and potential impacts.
- Hurricane Warning Systems: Hurricane warning systems are designed to provide timely and accurate information to the public about approaching hurricanes, including warnings of impending landfall.
- Hurricane Preparedness: Hurricane preparedness involves taking proactive steps to mitigate the potential impacts of a hurricane, including securing homes, preparing emergency kits, and developing evacuation plans.
2. Tropical Cyclone Landfall:
- Tropical Cyclone Formation: Tropical cyclones form over warm ocean waters and require specific atmospheric conditions, including low wind shear and pre-existing weather disturbances.
- Tropical Cyclone Structure: Tropical cyclones have a distinct structure, with a central eye surrounded by a rotating band of thunderstorms.
- Tropical Cyclone Categories: Tropical cyclones are categorized based on their wind speed, with different classifications used in various regions around the world.
- Tropical Cyclone Tracking: Tropical cyclone tracking involves monitoring the movement and intensity of tropical cyclones using satellite imagery, radar data, and weather models.
- Tropical Cyclone Warnings: Tropical cyclone warnings are issued to alert the public about the potential impacts of an approaching tropical cyclone, including the possibility of landfall.
3. Landfall Prediction:
- Weather Models: Weather models are computer programs that use mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and predict weather events, including landfall.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery provides valuable data on the location, intensity, and movement of storms, assisting in predicting landfall.
- Radar Data: Radar data provides information on precipitation patterns, wind speeds, and storm structure, helping to predict landfall.
- Data Assimilation: Data assimilation involves combining data from various sources, including weather models, satellite imagery, and radar data, to improve the accuracy of landfall predictions.
- Ensemble Forecasting: Ensemble forecasting involves running multiple weather models with slightly different starting conditions to account for uncertainties and provide a range of potential outcomes for landfall.
4. Landfall Impact Assessment:
- Storm Surge Modeling: Storm surge modeling uses computer simulations to predict the potential height and extent of storm surge associated with a hurricane landfall.
- Wind Field Analysis: Wind field analysis involves mapping the wind speeds and direction associated with a hurricane, providing information on the potential impact of high winds during landfall.
- Rainfall Estimation: Rainfall estimation uses weather models and data analysis to predict the amount of rainfall expected during a hurricane landfall.
- Damage Assessment: Damage assessment involves evaluating the extent of damage caused by a hurricane landfall, including infrastructure, property, and human lives.
- Risk Assessment: Risk assessment involves evaluating the potential risks associated with a hurricane landfall, considering factors such as storm intensity, population density, and infrastructure vulnerability.
5. Landfall Mitigation:
- Coastal Protection: Coastal protection measures, such as seawalls, breakwaters, and beach nourishment, can help to mitigate the impacts of storm surge and coastal erosion during landfall.
- Flood Control: Flood control measures, such as drainage systems, levees, and floodgates, can help to reduce the risk of flooding during landfall.
- Building Codes: Building codes can help to ensure that structures are built to withstand hurricane-force winds and storm surge during landfall.
- Early Warning Systems: Early warning systems, such as weather alerts, sirens, and public announcements, can help to alert residents to the threat of an approaching hurricane and provide time to prepare for landfall.
- Evacuation Procedures: Evacuation procedures are essential for ensuring the safety of residents in areas threatened by a hurricane landfall.
6. Landfall Recovery:
- Emergency Response: Emergency response efforts are crucial in the immediate aftermath of a hurricane landfall to provide medical care, shelter, and essential supplies to affected populations.
- Infrastructure Repair: Repairing damaged infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and power lines, is essential for restoring transportation, communication, and essential services after a hurricane landfall.
- Economic Recovery: Economic recovery efforts focus on rebuilding businesses, restoring jobs, and supporting the local economy after a hurricane landfall.
- Community Resilience: Building community resilience involves taking steps to prepare for future hurricane landfall and minimize the impacts on individuals, communities, and the environment.
7. Landfall and Climate Change:
- Sea Level Rise: Climate change is causing sea levels to rise, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and storm surge during hurricane landfall.
- Hurricane Intensity: Climate change is also linked to an increase in the intensity of hurricanes, potentially leading to more destructive landfall events.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Adapting to the impacts of climate change on hurricanes and landfall involves taking steps to reduce vulnerability and enhance resilience in coastal communities.
8. Landfall History:
- Historical Landfalls: Historical records provide valuable insights into the frequency, intensity, and impacts of hurricanes and other tropical cyclones over time.
- Notable Landfalls: Some landfall events have left a lasting mark on history, due to their intensity, devastation, and impact on human lives and infrastructure.
- Landfall Data Analysis: Analyzing historical landfall data can help to understand trends, patterns, and potential future risks.
FAQs by Landfall:
1. What is the difference between a hurricane and a tropical storm?
A hurricane is a type of tropical cyclone with sustained wind speeds of at least 74 mph. Tropical storms have wind speeds between 39 and 73 mph. Both can cause significant damage and disruption upon landfall, but hurricanes pose a greater threat due to their higher wind speeds and potential for storm surge.
2. How are hurricanes tracked?
Hurricanes are tracked using a combination of satellite imagery, radar data, and weather models. These tools provide information on the storm’s location, intensity, and projected path, allowing meteorologists to predict the potential for landfall and issue warnings.
3. What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale?
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a five-category system used to classify hurricane intensity based on their sustained wind speeds. Category 1 hurricanes have wind speeds of 74-95 mph, while Category 5 hurricanes have wind speeds of over 157 mph.
4. What is storm surge?
Storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the strong winds of a hurricane pushing water towards the shore. It can inundate coastal areas, causing significant flooding and damage, even in areas not directly hit by the eye of the storm.
5. How can I prepare for a hurricane landfall?
Preparing for a hurricane landfall involves taking proactive steps to mitigate the potential impacts. This includes securing your home, preparing an emergency kit, developing an evacuation plan, and staying informed about the latest forecasts and warnings.
6. What should I do if a hurricane warning is issued?
If a hurricane warning is issued, it’s crucial to take immediate action. This includes securing your home, preparing your emergency kit, listening to local authorities for instructions, and considering evacuation if advised.
7. How can I stay safe during a hurricane landfall?
During a hurricane landfall, it’s important to stay indoors and avoid unnecessary travel. If you are in a coastal area, seek higher ground to avoid storm surge. Stay informed about the latest weather updates and follow instructions from local authorities.
8. What are some of the long-term impacts of hurricane landfall?
Hurricane landfall can have significant long-term impacts, including economic losses, infrastructure damage, environmental degradation, and psychological trauma. Recovery efforts can take months or even years, requiring significant resources and community involvement.
Tips by Landfall:
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources, such as the National Weather Service.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Prepare an emergency kit that includes food, water, medication, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, batteries, and a weather radio.
- Secure Your Home: Secure your home by boarding up windows, trimming trees, and securing loose objects that could become projectiles.
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Develop an evacuation plan that includes identifying safe routes and designated meeting points.
- Listen to Local Authorities: Listen to local authorities for instructions and warnings, and follow their guidance during a hurricane landfall.
- Stay Indoors: Stay indoors during a hurricane landfall and avoid unnecessary travel.
- Seek Higher Ground: If you are in a coastal area, seek higher ground to avoid storm surge.
- Be Aware of Flooding: Be aware of the potential for flooding and avoid areas that are known to flood.
- Check on Your Neighbors: Check on your neighbors, especially those who may be elderly, disabled, or have special needs.
- Be Patient and Cooperative: Be patient and cooperative with emergency responders and other authorities.
Conclusion by Landfall:
Landfall marks a significant moment in the life cycle of a tropical cyclone, bringing with it the potential for widespread destruction and disruption. Understanding the impacts of landfall, preparing for its arrival, and mitigating its effects are crucial steps in protecting lives, property, and the environment. By staying informed, taking proactive measures, and working together, communities can enhance their resilience to the devastating consequences of landfall.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Landfall: Where the Storm Meets the Shore. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
