The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge
Related Articles: The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge
- 3.1 Unveiling the Mechanism: How Reverse Storm Surge Occurs
- 3.2 The Impact of Reverse Storm Surge: A Double-Edged Sword
- 3.3 Exploring Related Searches: Delving Deeper into the Dynamics of Reverse Storm Surge
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions About Reverse Storm Surge
- 3.5 Tips for Coastal Communities Facing Reverse Storm Surge
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Unseen Force Shaping Coastlines
- 4 Closure
The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge

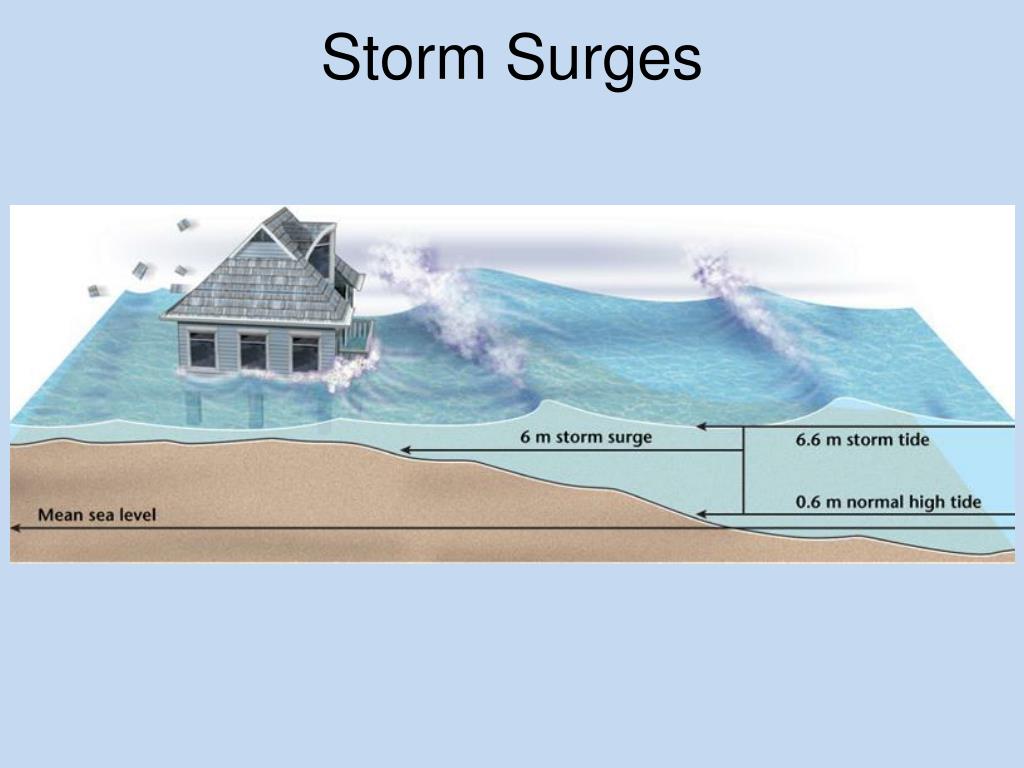
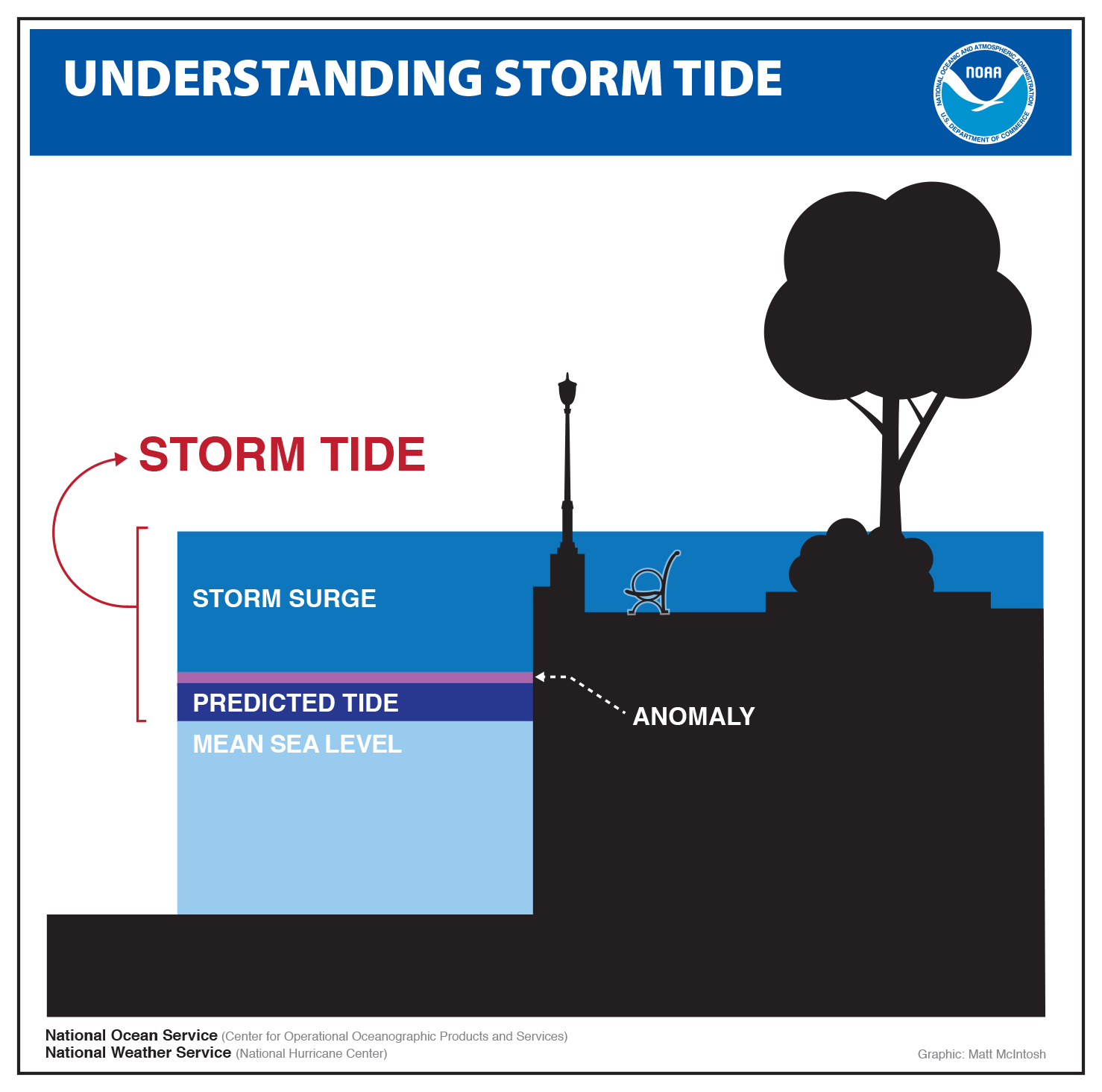
While the term "storm surge" conjures images of devastating floods and rising water levels, a lesser-known phenomenon exists: reverse storm surge. This seemingly paradoxical event, often described as a "negative surge," involves a decrease in water levels, creating a low tide effect during a storm. While not as widely discussed as its destructive counterpart, reverse storm surge plays a crucial role in coastal environments, offering unique benefits and posing distinct challenges.
Unveiling the Mechanism: How Reverse Storm Surge Occurs
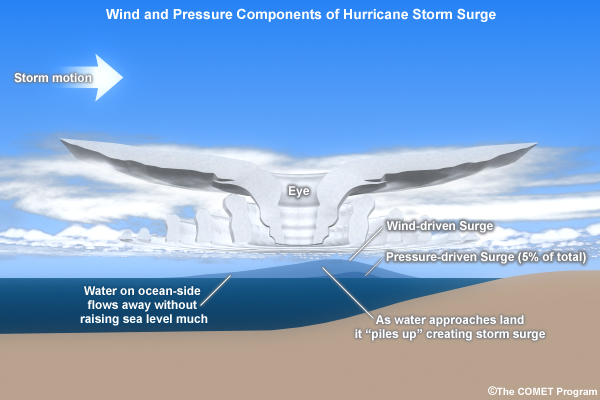
Reverse storm surge occurs when a combination of meteorological and oceanographic factors creates a pressure gradient that pulls water away from the coastline. This process is distinct from the typical storm surge, which is driven by the wind pushing water towards the shore. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
- Wind Direction: Reverse storm surge often occurs when strong winds blow offshore, pushing water away from the coast. This wind pattern can be associated with specific weather systems, such as offshore low-pressure systems or strong high-pressure systems.
- Atmospheric Pressure: Low atmospheric pressure over the ocean can create a "suction" effect, pulling water upwards. This effect is magnified when the pressure gradient between the ocean and the coast is significant.
- Oceanographic Conditions: The presence of strong currents or upwelling events can further contribute to reverse storm surge. These factors can draw water away from the coastline, enhancing the low tide effect.
The Impact of Reverse Storm Surge: A Double-Edged Sword
While reverse storm surge might seem like a positive phenomenon, its impact is multifaceted, offering both potential benefits and drawbacks:
Benefits:
- Increased Navigation: Reverse storm surge can temporarily deepen channels and harbors, facilitating navigation for ships and boats. This can be particularly beneficial for ports and coastal communities reliant on maritime trade.
- Enhanced Beach Access: Reverse storm surge can expose larger areas of beach, providing opportunities for recreation and leisure activities.
- Reduced Flooding Risk: In areas prone to storm surge flooding, reverse storm surge can temporarily alleviate flooding risks by lowering water levels.
Drawbacks:
- Coastal Erosion: The receding water levels associated with reverse storm surge can expose coastal areas to increased erosion, especially during storms.
- Marine Ecosystem Impacts: Reverse storm surge can disrupt marine ecosystems by altering water flow patterns and exposing organisms to changing environmental conditions.
- Saltwater Intrusion: In coastal aquifers, reverse storm surge can lead to saltwater intrusion, contaminating freshwater sources.
Exploring Related Searches: Delving Deeper into the Dynamics of Reverse Storm Surge
Understanding reverse storm surge requires exploring its various aspects and related concepts. Here’s a detailed examination of eight common related searches:
-
Reverse Storm Surge vs. Storm Surge:
- Storm surge: A rise in sea level caused by the wind pushing water towards the shore.
- Reverse storm surge: A decrease in sea level caused by winds pushing water away from the shore.
- Key Differences: The direction of wind and the resulting water level change differentiate the two phenomena.
- Impact: While storm surge leads to flooding and coastal damage, reverse storm surge can create opportunities for navigation and beach access, but also pose risks like erosion and ecosystem disruption.
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Coastal Erosion:
- Mechanism: Reverse storm surge can exacerbate coastal erosion by exposing the shoreline to stronger wave action and reducing the natural protection provided by sandbars and dunes.
- Impact: Coastal erosion can lead to property damage, loss of beach habitat, and displacement of coastal communities.
- Mitigation Strategies: Protecting coastal areas with seawalls, breakwaters, and beach nourishment programs can help mitigate erosion.
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Marine Ecosystems:
- Impact: Reverse storm surge can alter water flow patterns, salinity levels, and sediment transport, impacting marine ecosystems.
-
Examples:
- Mangrove forests: Reverse storm surge can lead to increased salinity levels, affecting mangrove growth and survival.
- Coral reefs: The receding water levels can expose corals to air and sunlight, leading to bleaching and mortality.
- Fish populations: Reverse storm surge can disrupt fish spawning and migration patterns, impacting population dynamics.
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Saltwater Intrusion:
- Mechanism: Reverse storm surge can push saltwater inland, contaminating freshwater aquifers.
- Impact: Saltwater intrusion can make freshwater sources unusable for drinking, irrigation, and other purposes.
- Mitigation Strategies: Implementing water management practices, such as controlled pumping and barrier systems, can help prevent saltwater intrusion.
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Coastal Communities:
-
Impact: Reverse storm surge can affect coastal communities in various ways, including:
- Navigation: Increased access to ports and harbors.
- Recreation: Expanded beach access for tourism and leisure activities.
- Infrastructure: Exposure of coastal infrastructure to erosion and saltwater intrusion.
- Economic activity: Impacts on fishing, tourism, and other industries.
-
Impact: Reverse storm surge can affect coastal communities in various ways, including:
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Climate Change:
- Potential Impacts: Climate change is expected to alter weather patterns and oceanographic conditions, potentially influencing the frequency and intensity of reverse storm surge.
- Research: Further research is needed to understand how climate change will impact the occurrence and consequences of reverse storm surge.
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Forecasting:
- Challenges: Forecasting reverse storm surge is more complex than predicting typical storm surge due to the intricate interplay of meteorological and oceanographic factors.
- Importance: Accurate forecasting of reverse storm surge is crucial for coastal communities to prepare for potential impacts and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
-
Reverse Storm Surge and Research:
- Current Research: Scientists are actively studying reverse storm surge to better understand its mechanisms, impacts, and forecasting capabilities.
- Future Research: Research efforts will focus on developing improved forecasting models, assessing the long-term effects of reverse storm surge on coastal ecosystems, and developing sustainable management strategies for coastal areas.
Frequently Asked Questions About Reverse Storm Surge
Q: Can reverse storm surge be predicted?
A: Predicting reverse storm surge is more complex than predicting typical storm surge due to the interplay of multiple factors. However, advancements in weather forecasting and oceanographic modeling are improving prediction capabilities.
Q: How does reverse storm surge differ from a low tide?
A: Reverse storm surge is a temporary drop in sea level caused by specific meteorological conditions, while low tide is a regular, predictable occurrence driven by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun.
Q: Is reverse storm surge a common phenomenon?
A: Reverse storm surge is less common than typical storm surge, but it can occur in various coastal regions, particularly along open coastlines and in areas with strong offshore winds.
Q: Can reverse storm surge be harmful?
A: While reverse storm surge can offer benefits, it can also have negative impacts, such as coastal erosion, saltwater intrusion, and disruption of marine ecosystems.
Q: What measures can be taken to mitigate the negative impacts of reverse storm surge?
A: Coastal communities can implement measures like seawalls, breakwaters, and beach nourishment to mitigate erosion, and employ water management practices to prevent saltwater intrusion.
Tips for Coastal Communities Facing Reverse Storm Surge
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and advisories for potential reverse storm surge events.
- Prepare for Erosion: Implement erosion control measures and maintain coastal infrastructure.
- Protect Freshwater Resources: Implement strategies to prevent saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers.
- Adapt to Changing Conditions: Coastal communities need to adapt to the potential impacts of reverse storm surge on their infrastructure, economies, and ecosystems.
Conclusion: The Unseen Force Shaping Coastlines
Reverse storm surge, a seemingly paradoxical phenomenon, plays a vital role in shaping coastal environments. While it might not be as widely recognized as its destructive counterpart, its influence on navigation, coastal erosion, marine ecosystems, and freshwater resources is undeniable. As we strive to understand and adapt to the complex dynamics of coastal regions, recognizing the significance of reverse storm surge is crucial for managing and protecting our coastlines for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Counterintuitive Force: Understanding Reverse Storm Surge. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
