The Power of Managed Care Organizations: Optimizing Healthcare Delivery
Related Articles: The Power of Managed Care Organizations: Optimizing Healthcare Delivery
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Managed Care Organizations: Optimizing Healthcare Delivery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Managed Care Organizations: Optimizing Healthcare Delivery

Managed care organizations (MCOs) have emerged as a pivotal force in the healthcare landscape, revolutionizing how medical services are delivered and financed. Their impact is multifaceted, influencing patient access to care, healthcare costs, and the overall quality of medical outcomes. This article delves into the intricacies of MCOs, exploring their structure, functions, and the profound implications they have on the healthcare system.
Understanding Managed Care Organizations
MCOs are healthcare organizations that manage the delivery of medical services to a defined group of individuals, typically through a network of healthcare providers. Their core function is to streamline healthcare access while controlling costs, emphasizing preventative care, and promoting patient health.
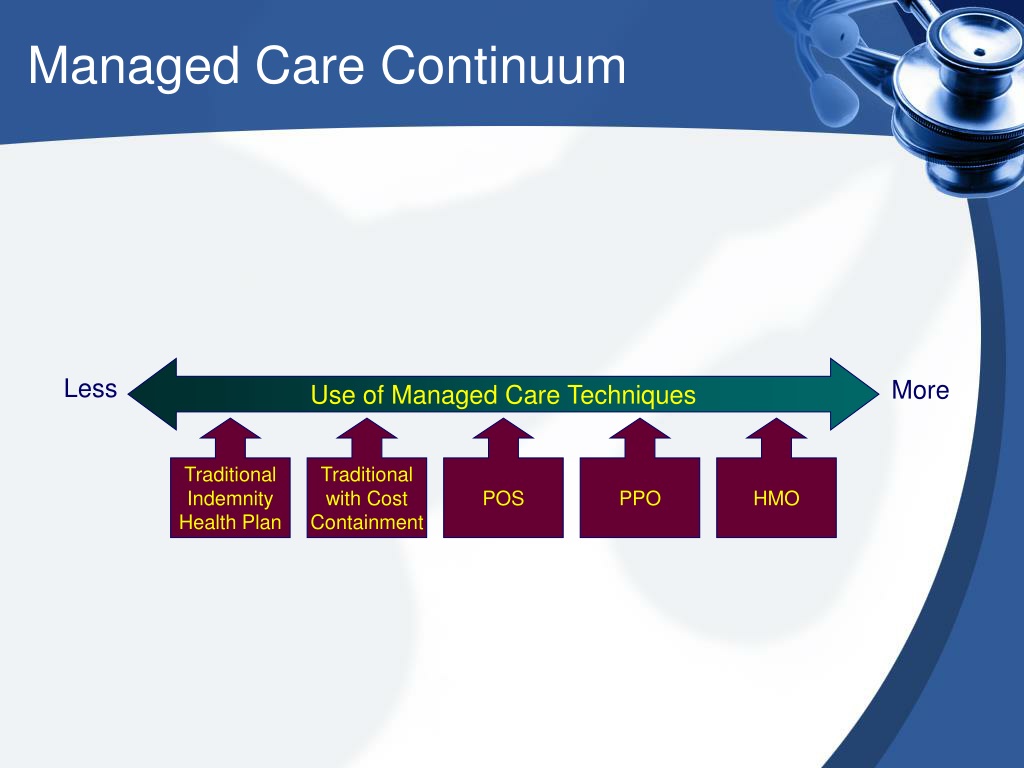
Types of MCOs
Several distinct types of MCOs operate within the healthcare system, each with its unique characteristics and focus:
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs operate on a closed-panel system, requiring members to select a primary care physician (PCP) within the network. Patients need referrals from their PCP to see specialists. HMOs typically emphasize preventive care and cost control.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer greater flexibility than HMOs. Members can choose healthcare providers both inside and outside the network, although costs are generally lower for in-network services.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs. Members select a PCP but can access out-of-network providers for a higher cost.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs are similar to HMOs but offer fewer network options. Members must choose providers within the network, and out-of-network services are typically not covered.
The Role of MCOs in Healthcare
MCOs play a crucial role in optimizing the healthcare system by:
- Managing Costs: MCOs utilize various strategies to control costs, including negotiating lower rates with providers, promoting preventive care, and managing utilization of services.
- Improving Quality: MCOs often implement quality improvement initiatives, such as disease management programs, to enhance patient outcomes and reduce complications.
- Expanding Access: MCOs can improve access to care, particularly for underserved populations, by providing a network of providers and coordinating care.
- Promoting Patient Health: MCOs encourage preventive care and health education programs, aiming to improve patient health and reduce the need for costly treatments.
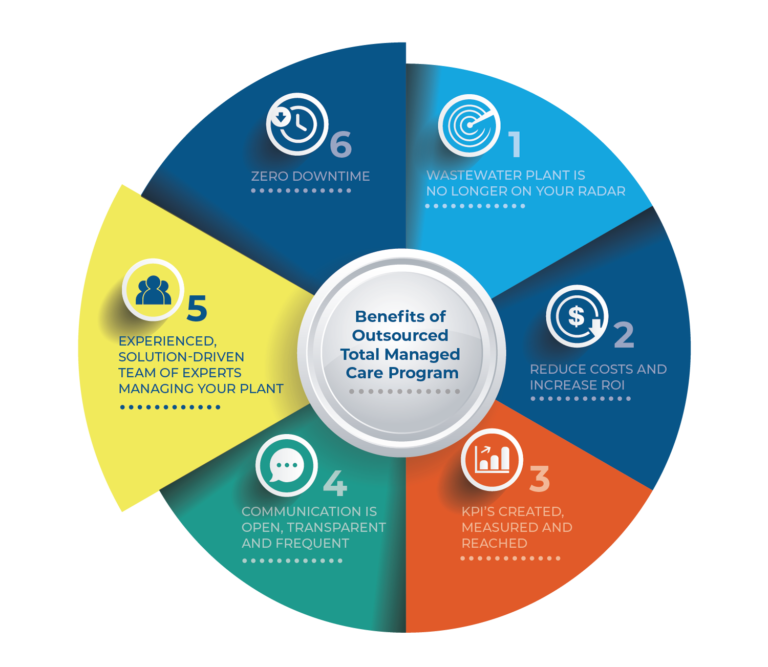
Benefits of MCOs
The benefits of MCOs are numerous and far-reaching, impacting both patients and the healthcare system as a whole:
- Lower Healthcare Costs: MCOs contribute to lower healthcare costs by negotiating lower rates with providers and managing utilization of services.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: MCOs often implement quality improvement programs that lead to better patient outcomes and reduced complications.
- Increased Access to Care: MCOs can expand access to care by providing a network of providers and coordinating care, particularly for underserved populations.
- Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: MCOs can lead to improved patient satisfaction by providing easier access to care, personalized treatment plans, and better communication with providers.
Challenges of MCOs
Despite their benefits, MCOs also face several challenges:
- Limited Provider Choice: Some MCOs, particularly HMOs, restrict patient choice by requiring them to select providers from a closed network.
- Potential for Reduced Quality: In some instances, cost-cutting measures implemented by MCOs may lead to a reduction in the quality of care.
- Administrative Complexity: MCOs can introduce administrative complexity for both patients and providers, leading to potential delays and frustrations.
The Future of MCOs
The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, and MCOs are adapting to these changes. Key trends impacting the future of MCOs include:
- Integration of Technology: MCOs are increasingly integrating technology to improve care coordination, patient engagement, and data analytics.
- Focus on Value-Based Care: MCOs are shifting towards value-based care models that incentivize providers to improve quality and reduce costs.
- Expansion of Telehealth: MCOs are incorporating telehealth services to expand access to care and reduce the need for in-person visits.
Related Searches
1. Managed Care Organization vs. Insurance Company:
While often used interchangeably, MCOs and insurance companies have distinct functions. Insurance companies primarily cover healthcare costs, while MCOs manage the delivery of healthcare services. MCOs can act as insurers, but their primary focus is on healthcare delivery and management.
2. Managed Care Organization vs. PPO:
MCOs encompass a broader range of healthcare delivery models, including PPOs. PPOs are a specific type of MCO that offers greater flexibility in choosing providers, but typically at a higher cost for out-of-network services.
3. Types of Managed Care Organizations:
As discussed earlier, several types of MCOs exist, including HMOs, PPOs, POS plans, and EPOs. Each type has its own unique characteristics and benefits, allowing patients to choose a plan that best suits their needs.
4. Managed Care Organization Examples:
Numerous MCOs operate across the United States, including national players like Anthem, UnitedHealthcare, and Humana, as well as regional organizations. Choosing an MCO depends on individual needs, coverage requirements, and network availability.
5. Managed Care Organization Network:
MCOs establish networks of healthcare providers, including physicians, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities, to deliver care to their members. The size and scope of the network vary depending on the MCO and geographic location.
6. Managed Care Organization vs. Traditional Healthcare:
Traditional healthcare systems typically involve fee-for-service models, where providers are paid for each service rendered. MCOs shift the focus from volume-based care to value-based care, emphasizing quality and cost-effectiveness.
7. Managed Care Organization and Medicare:
Medicare Advantage plans are a type of MCO offered through Medicare. These plans provide comprehensive coverage through a network of providers, often with additional benefits not covered by traditional Medicare.
8. Managed Care Organization and Medicaid:
Medicaid Managed Care programs are implemented in many states, where MCOs are contracted to provide healthcare services to Medicaid beneficiaries. These programs aim to improve access to care and manage costs within the Medicaid system.
FAQs about MCOs
1. What is the main purpose of an MCO?
The primary purpose of an MCO is to manage the delivery of healthcare services to a defined group of individuals, typically through a network of providers. MCOs aim to streamline healthcare access, control costs, emphasize preventive care, and promote patient health.
2. How do MCOs control costs?
MCOs employ various strategies to control costs, including:
- Negotiating lower rates with providers: MCOs leverage their large membership base to negotiate lower rates with healthcare providers, reducing the cost of services.
- Promoting preventive care: By encouraging preventive screenings and health education, MCOs aim to reduce the need for costly treatments later on.
- Managing utilization of services: MCOs monitor the use of healthcare services, ensuring appropriate and cost-effective care is provided.
3. What are the benefits of joining an MCO?
Joining an MCO can offer several benefits, including:
- Lower healthcare costs: MCOs typically offer lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses compared to traditional health insurance plans.
- Improved quality of care: MCOs often implement quality improvement programs that lead to better patient outcomes and reduced complications.
- Increased access to care: MCOs can expand access to care by providing a network of providers and coordinating care, particularly for underserved populations.
4. What are the drawbacks of joining an MCO?
While MCOs offer numerous benefits, they also have potential drawbacks:
- Limited provider choice: Some MCOs restrict patient choice by requiring them to select providers from a closed network.
- Potential for reduced quality: In some instances, cost-cutting measures implemented by MCOs may lead to a reduction in the quality of care.
- Administrative complexity: MCOs can introduce administrative complexity for both patients and providers, leading to potential delays and frustrations.
5. How do I choose the right MCO for me?
Choosing the right MCO depends on individual needs, coverage requirements, and network availability. Consider factors such as:
- Coverage: Does the plan cover the services you need, such as prescription drugs, mental health care, and preventive screenings?
- Network: Does the plan include providers you trust and are convenient for you?
- Cost: What are the premiums, deductibles, and co-pays?
- Customer service: How responsive and helpful is the MCO’s customer service?
Tips for Navigating MCOs
- Understand your plan: Carefully review your MCO plan documents to understand your coverage, benefits, and limitations.
- Choose a PCP: Select a PCP within the network who you trust and can manage your overall healthcare needs.
- Use in-network providers: Whenever possible, use in-network providers to minimize out-of-pocket costs.
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your MCO or providers questions about your coverage, benefits, and treatment options.
- Stay informed: Stay updated on changes to your plan, network, and coverage.
Conclusion
Managed care organizations (MCOs) have significantly impacted the healthcare landscape, transforming the delivery and financing of medical services. While they face challenges, MCOs offer numerous benefits, including cost control, quality improvement, and expanded access to care. As healthcare continues to evolve, MCOs are adapting to new technologies, value-based care models, and the growing demand for telehealth services. Understanding the complexities of MCOs is crucial for navigating the healthcare system effectively and maximizing the benefits they offer.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Managed Care Organizations: Optimizing Healthcare Delivery. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
