The Power of Nature: Understanding Hurricane Formation and Impact
Related Articles: The Power of Nature: Understanding Hurricane Formation and Impact
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Nature: Understanding Hurricane Formation and Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Nature: Understanding Hurricane Formation and Impact

Hurricanes, also known as typhoons or cyclones, are nature’s most powerful storms. They are characterized by intense, rotating systems of thunderstorms, generating sustained winds of at least 74 miles per hour (119 kilometers per hour). These powerful storms can cause catastrophic damage to coastal areas, impacting millions of lives and disrupting economies worldwide.
Formation and Structure:
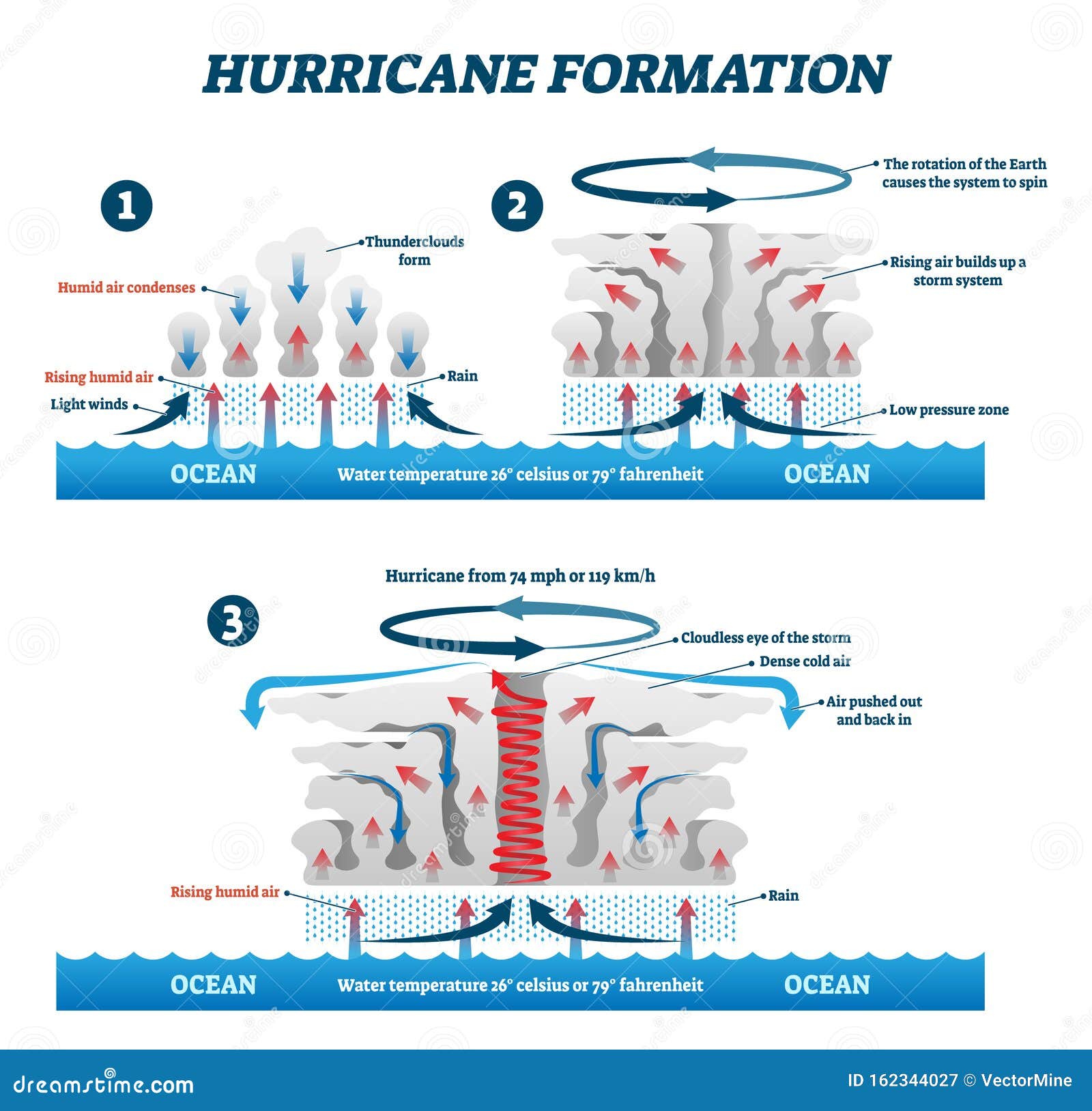
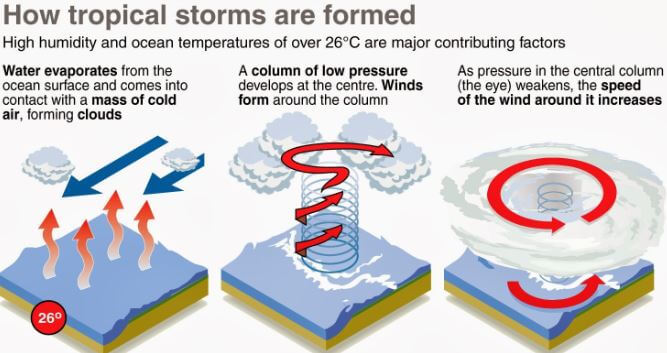
Hurricanes develop over warm ocean waters, typically in tropical or subtropical regions. The key ingredients for their formation are:
- Warm Ocean Water: The ocean surface must be at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius) to provide the necessary heat and moisture.
- Low Wind Shear: Vertical wind shear, the change in wind speed and direction with height, must be minimal to allow the storm to develop vertically.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: A pre-existing weather disturbance, such as a tropical wave or a cluster of thunderstorms, acts as a seed for the developing hurricane.
As the warm, moist air rises, it cools and condenses, releasing latent heat. This process fuels the storm, creating a cycle of rising air and descending air, leading to the formation of a powerful rotating vortex.
Hurricanes are characterized by a distinct structure:
- Eye: The calm center of the hurricane, often cloud-free and relatively calm.
- Eyewall: A ring of intense thunderstorms surrounding the eye, producing the strongest winds and heaviest rainfall.
- Spiral Bands: Bands of thunderstorms that extend outward from the eyewall, bringing heavy rain and strong winds.
Hurricanes are classified into five categories based on their wind speed, using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. Category 1 storms have wind speeds of 74-95 mph, while Category 5 storms have wind speeds exceeding 157 mph.
Impacts and Hazards:
Hurricanes cause significant damage and pose various hazards:
- Strong Winds: High-velocity winds can cause widespread structural damage, uproot trees, and generate flying debris, leading to injuries and fatalities.
- Storm Surge: The rise in sea level caused by the hurricane‘s powerful winds pushing water toward the shore can inundate coastal areas, causing flooding and erosion.
- Heavy Rainfall: Intense rainfall can lead to flash floods, landslides, and widespread property damage.
- Tornadoes: Hurricanes can spawn tornadoes, adding to the destructive potential of the storm.
Hurricanes also have significant economic and social impacts, disrupting transportation, power grids, and communication systems, leading to widespread business closures and displacement of populations.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Season:
The Atlantic hurricane season officially runs from June 1st to November 30th, with the peak activity occurring in late August and September. The Pacific hurricane season runs from May 15th to November 30th, with the peak activity occurring in late August and early September. Understanding the hurricane season allows for better preparation and mitigation efforts.
2. Hurricane Tracking:
Advanced weather satellites, radar systems, and computer models are used to track hurricanes, providing valuable data for forecasting their path and intensity. This information enables authorities to issue timely warnings and evacuate vulnerable areas, minimizing the impact of the storm.
3. Hurricane Preparedness:
Preparing for a hurricane is crucial for protecting life and property. This includes securing homes, stocking up on essential supplies, and having a communication plan in place. Communities and individuals must be proactive in their preparedness efforts.
4. Hurricane Mitigation:
Mitigation measures aim to reduce the potential damage caused by hurricanes. This includes strengthening infrastructure, building seawalls, and promoting sustainable land use practices. By taking proactive steps, communities can enhance their resilience to these powerful storms.
5. Hurricane Recovery:
After a hurricane strikes, the focus shifts to recovery and rebuilding. This involves providing emergency aid, restoring infrastructure, and supporting affected communities in their recovery efforts.
6. Hurricane History:
Analyzing historical hurricane data provides valuable insights into their frequency, intensity, and impact. This information helps researchers understand climate change’s influence on hurricane activity and improve forecasting models.
7. Hurricane Research:
Scientists are constantly researching hurricanes to improve our understanding of their formation, behavior, and impact. This research leads to advancements in forecasting, mitigation, and preparedness strategies.
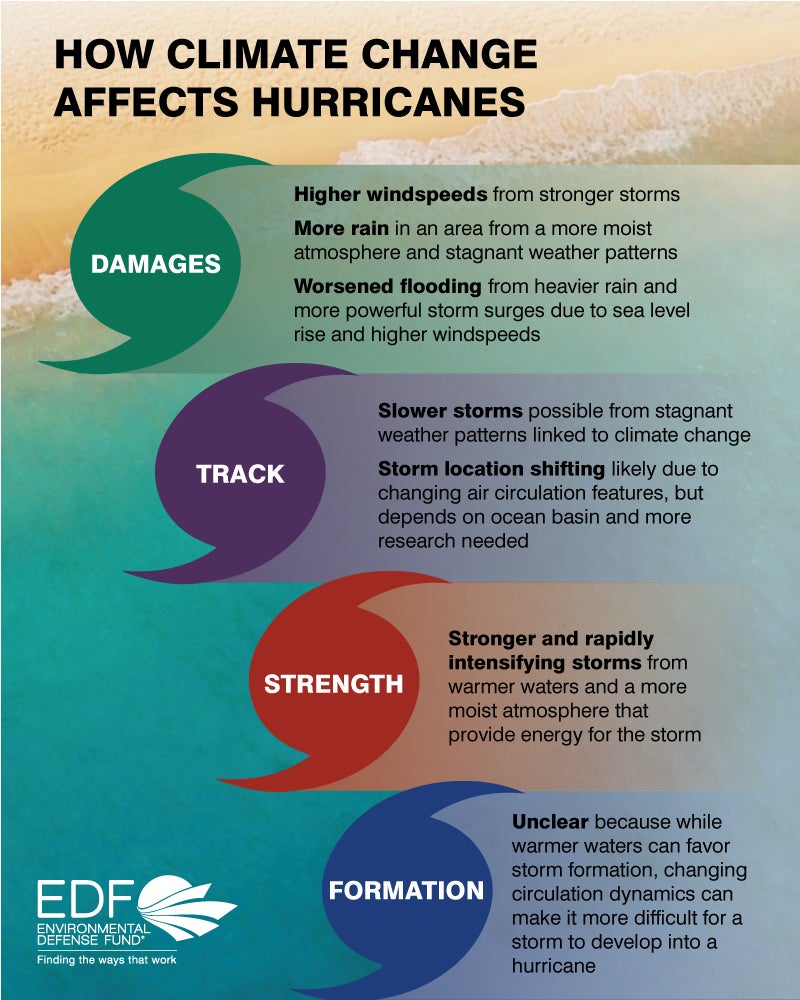
8. Hurricane Impact on Climate Change:
Climate change is expected to influence the intensity and frequency of hurricanes. Rising sea levels, warmer ocean temperatures, and changes in atmospheric circulation patterns can contribute to more intense and frequent storms.
FAQs About Hurricanes:
1. What is the difference between a hurricane, typhoon, and cyclone?
These terms refer to the same type of storm but are used in different parts of the world. Hurricane is used in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific basins, typhoon in the Northwest Pacific basin, and cyclone in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean basins.
2. How are hurricanes formed?
Hurricanes form over warm ocean waters when certain conditions are met, including warm ocean temperatures, low wind shear, and a pre-existing disturbance.
3. What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale?
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale classifies hurricanes into five categories based on their wind speed, with Category 5 being the most intense.
4. What are the main hazards associated with hurricanes?
Hurricanes pose various hazards, including strong winds, storm surge, heavy rainfall, and tornadoes.
5. How can I prepare for a hurricane?
Preparing for a hurricane involves securing your home, stocking up on essential supplies, and having a communication plan in place.
6. What are some hurricane mitigation strategies?
Mitigation strategies include strengthening infrastructure, building seawalls, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
7. How does climate change impact hurricanes?
Climate change is expected to influence the intensity and frequency of hurricanes, leading to more intense and frequent storms.
8. What are some tips for staying safe during a hurricane?
During a hurricane, it is crucial to stay indoors, listen to weather updates, and follow evacuation orders if issued.
Tips for Staying Safe During a Hurricane:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and heed warnings from local authorities.
- Secure Your Home: Secure loose objects, board up windows, and prepare a safe room.
- Stock Up on Supplies: Gather enough food, water, medicine, and other essentials for several days.
- Have a Communication Plan: Establish a way to communicate with family and friends before, during, and after the storm.
- Evacuate If Ordered: If ordered to evacuate, do so immediately and follow designated routes.
- Stay Inside: During the storm, stay indoors in a safe room or the lowest floor of your home.
- Avoid Floodwaters: Do not attempt to drive or walk through floodwaters.
- Be Aware of Debris: Use caution when walking or driving after the storm, as debris can be hazardous.
Conclusion:
Hurricanes are powerful natural phenomena that pose significant risks to coastal communities. Understanding their formation, impacts, and hazards is essential for effective preparedness, mitigation, and response. By staying informed, taking necessary precautions, and working together, we can minimize the devastating effects of these storms and build more resilient communities.
Hurricanes are a reminder of the immense power of nature and the importance of respecting its forces. By understanding these powerful storms, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from their destructive potential.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Nature: Understanding Hurricane Formation and Impact. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
