The Sudden Fury of Water: Understanding and Mitigating Flash Floods
Related Articles: The Sudden Fury of Water: Understanding and Mitigating Flash Floods
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Sudden Fury of Water: Understanding and Mitigating Flash Floods. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sudden Fury of Water: Understanding and Mitigating Flash Floods

Flash floods, characterized by their rapid onset and overwhelming force, are a potent reminder of nature’s unpredictable power. These sudden surges of water, often transforming dry landscapes into raging torrents within minutes, pose a significant threat to human life and infrastructure. This article delves into the intricacies of flash floods, exploring their causes, impacts, and the crucial steps we can take to mitigate their devastating effects.
Understanding the Genesis of Flash Floods
Flash floods are not merely a result of heavy rainfall. They are a complex phenomenon driven by a confluence of factors, including:
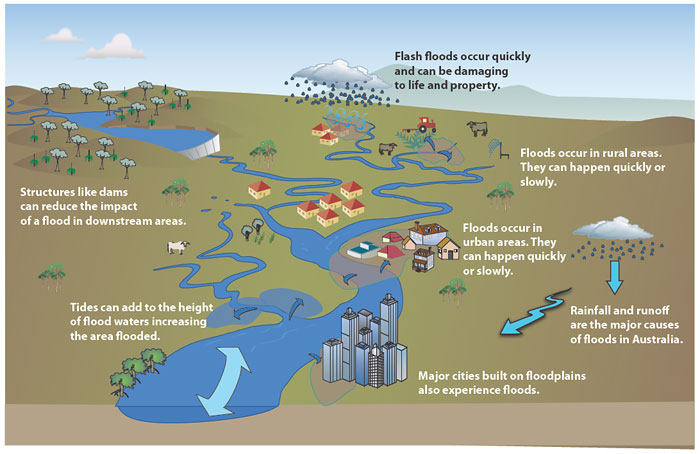
- Intense Rainfall: While rain is a prerequisite, it’s the intensity, not the duration, that fuels flash floods. A sudden downpour, especially over saturated ground, can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to rapid water accumulation.
- Terrain and Topography: Steep slopes and narrow valleys accelerate the flow of water, concentrating its force and increasing the risk of flash floods.
- Urbanization: The proliferation of impervious surfaces, such as concrete and asphalt, in urban areas reduces the rate of water absorption into the ground. This leads to increased runoff, amplifying the potential for flash floods.
- Antecedent Moisture Conditions: Dry ground absorbs water readily, but when soil is already saturated from previous rainfall, the capacity for further absorption diminishes, making it more susceptible to flash floods.
- Dam or Levee Failures: The catastrophic failure of dams or levees can release massive amounts of water, leading to widespread flash floods in downstream areas.
The Devastating Impacts of Flash Floods
Flash floods are not merely a nuisance; they are a force of destruction, capable of inflicting significant damage on people, property, and the environment. The consequences of these sudden surges of water are multifaceted:
- Loss of Life: Flash floods are responsible for numerous fatalities each year. The rapid rise of water and strong currents can sweep people off their feet, rendering them vulnerable to drowning.
- Property Damage: Homes, businesses, and infrastructure are often severely damaged or destroyed by flash floods. The sheer force of the water can cause structural collapse, inundate buildings, and erode foundations.
- Economic Disruptions: Flash floods can cripple transportation networks, disrupt supply chains, and lead to significant economic losses. Businesses may be forced to close temporarily, and agricultural land can be rendered unusable.
- Environmental Degradation: Flash floods can erode soil, pollute waterways with debris and contaminants, and displace wildlife. The impact on ecosystems can be long-lasting and detrimental.
Mitigating the Risks of Flash Floods
While we cannot entirely eliminate the threat of flash floods, proactive measures can significantly reduce their impact. Effective mitigation strategies encompass:
- Early Warning Systems: Advanced weather forecasting and monitoring systems are crucial for issuing timely warnings of impending flash floods. These systems can alert communities and enable swift evacuation efforts.
- Flood Control Structures: Engineering solutions like dams, levees, and retention ponds can help manage water flow and prevent flash floods. However, these structures require careful design and maintenance to be effective.
- Land Use Planning: Restricting development in flood-prone areas and promoting sustainable land management practices can help minimize the risk of flash floods.
- Public Awareness and Education: Educating the public about the dangers of flash floods, the importance of preparedness, and the appropriate response during a flood event is paramount.
Related Searches: Flash Flood Insights
1. Flash Flood Forecasting:
Forecasting flash floods is a challenging but essential task. Meteorologists use sophisticated models and data analysis to predict the likelihood and severity of flash flood events. These models incorporate factors such as rainfall intensity, soil moisture, and terrain characteristics. Advances in radar technology, satellite imagery, and real-time data collection contribute to more accurate and timely forecasts.
2. Flash Flood Safety:
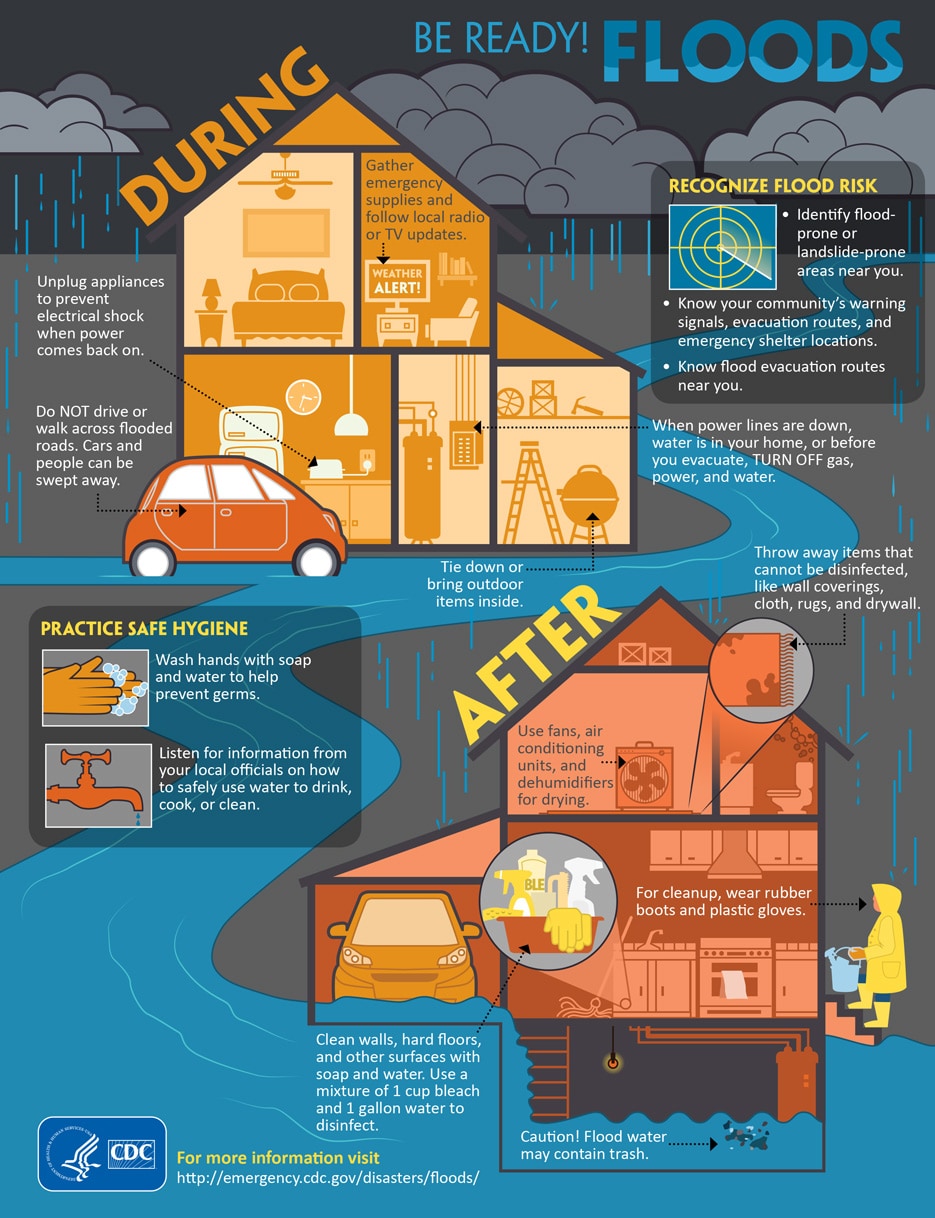
The best way to stay safe during a flash flood is to avoid areas prone to flooding. If caught in a flash flood, seek higher ground immediately and do not attempt to drive through flooded roads. Remember, "Turn Around, Don’t Drown."
3. Flash Flood Impacts on Agriculture:
Flash floods can devastate agricultural lands, causing crop loss, soil erosion, and contamination of water sources. Farmers can implement flood-resistant crops, utilize drainage systems, and implement crop insurance to mitigate the impact.
4. Flash Flood Mitigation in Urban Areas:
Urban areas are particularly susceptible to flash floods due to impervious surfaces and limited drainage. Mitigation strategies in urban environments include green infrastructure, stormwater management systems, and public awareness campaigns.
5. Flash Flood History and Notable Events:
Studying past flash flood events provides valuable insights into their frequency, severity, and impact. Notable events, such as the 1993 Mississippi River flood and the 2013 Colorado floods, highlight the devastating consequences of these natural disasters.
6. Flash Flood Risk Mapping:
Flood risk maps identify areas prone to flash floods, helping communities to understand their vulnerability and prioritize mitigation efforts. These maps integrate data on terrain, rainfall patterns, and historical flood events.
7. Flash Flood Response and Recovery:
Emergency response teams play a crucial role in rescuing people trapped by flash floods, providing medical assistance, and coordinating relief efforts. The recovery process involves infrastructure repair, debris removal, and economic support for affected communities.
8. Flash Flood Research and Innovation:
Ongoing research and innovation are crucial for improving our understanding of flash floods and developing more effective mitigation strategies. This includes advancements in forecasting models, flood control technologies, and public education initiatives.
FAQs about Flash Floods
Q: What is the difference between a flash flood and a regular flood?
A: While both involve excessive water accumulation, flash floods are characterized by their rapid onset and short duration. Regular floods typically develop over a longer period and may be caused by prolonged rainfall or river overflows.
Q: How can I prepare for a flash flood?
A: Develop a family emergency plan, including evacuation routes and a designated meeting point. Keep a supply kit with essential items such as water, food, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio. Stay informed about weather forecasts and warnings.
Q: What should I do if I encounter a flash flood?
A: Move to higher ground immediately. Do not attempt to drive through flooded roads, as water can be deeper than it appears. If trapped, seek higher ground or climb onto a sturdy object to stay above the water.
Q: Can climate change worsen flash floods?
A: Yes, climate change is expected to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including flash floods. Rising global temperatures can lead to more frequent and intense rainfall, increasing the risk of flash flood events.
Tips for Mitigating Flash Flood Risks
- Check your property’s flood risk: Consult flood maps and local authorities to determine your property’s vulnerability to flash floods.
- Elevate electrical outlets and appliances: This can reduce the risk of damage from rising floodwaters.
- Install sump pumps: Sump pumps can help remove excess water from basements and prevent flooding.
- Maintain gutters and downspouts: Clean and clear gutters and downspouts to ensure proper water drainage and reduce the risk of overflow.
- Plant trees and vegetation: Trees and vegetation can help absorb rainwater and slow down runoff, reducing the risk of flash floods.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Flash floods are a formidable force of nature, capable of wreaking havoc in a matter of minutes. While we cannot control the weather, we can take proactive steps to mitigate the risks and minimize the impact of these sudden surges of water. By understanding the causes, impacts, and mitigation strategies, we can better prepare for the unpredictable nature of flash floods and safeguard our communities. The key to mitigating the threat lies in a collective effort, encompassing effective forecasting, robust infrastructure, responsible land management, and informed public awareness.
Let us strive to build resilience against the fury of flash floods, ensuring the safety and well-being of our communities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sudden Fury of Water: Understanding and Mitigating Flash Floods. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
