Understanding Hurricane Strength: A Comprehensive Guide to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale
Related Articles: Understanding Hurricane Strength: A Comprehensive Guide to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Hurricane Strength: A Comprehensive Guide to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Hurricane Strength: A Comprehensive Guide to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale
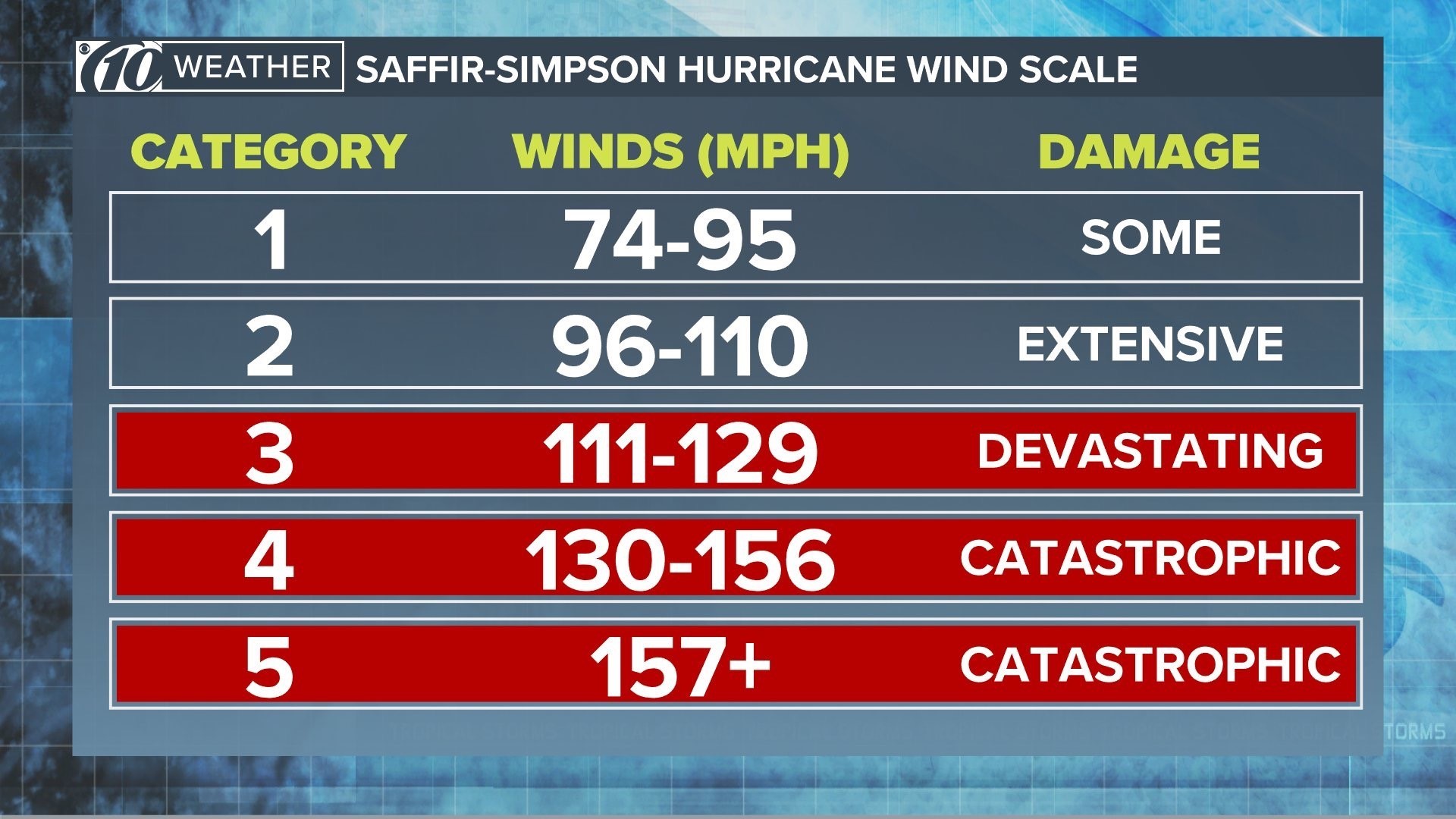
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a widely recognized tool for classifying the intensity of hurricanes based on their sustained wind speeds. This scale, developed by Herbert Saffir, a civil engineer, and Robert Simpson, a meteorologist, provides a clear and concise method for understanding the potential damage a hurricane can cause.
The Scale’s Structure:
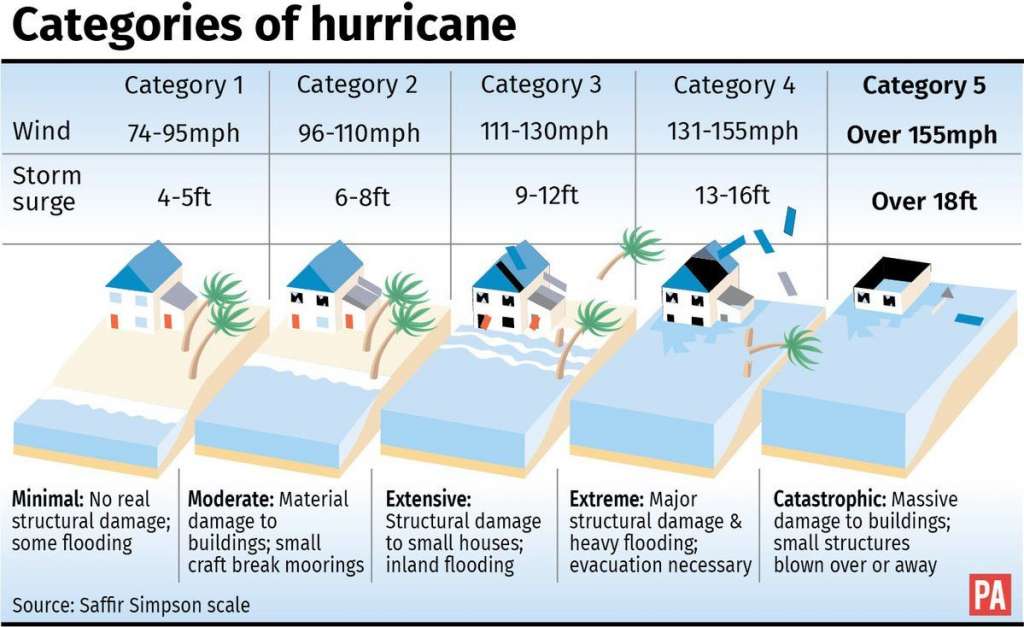
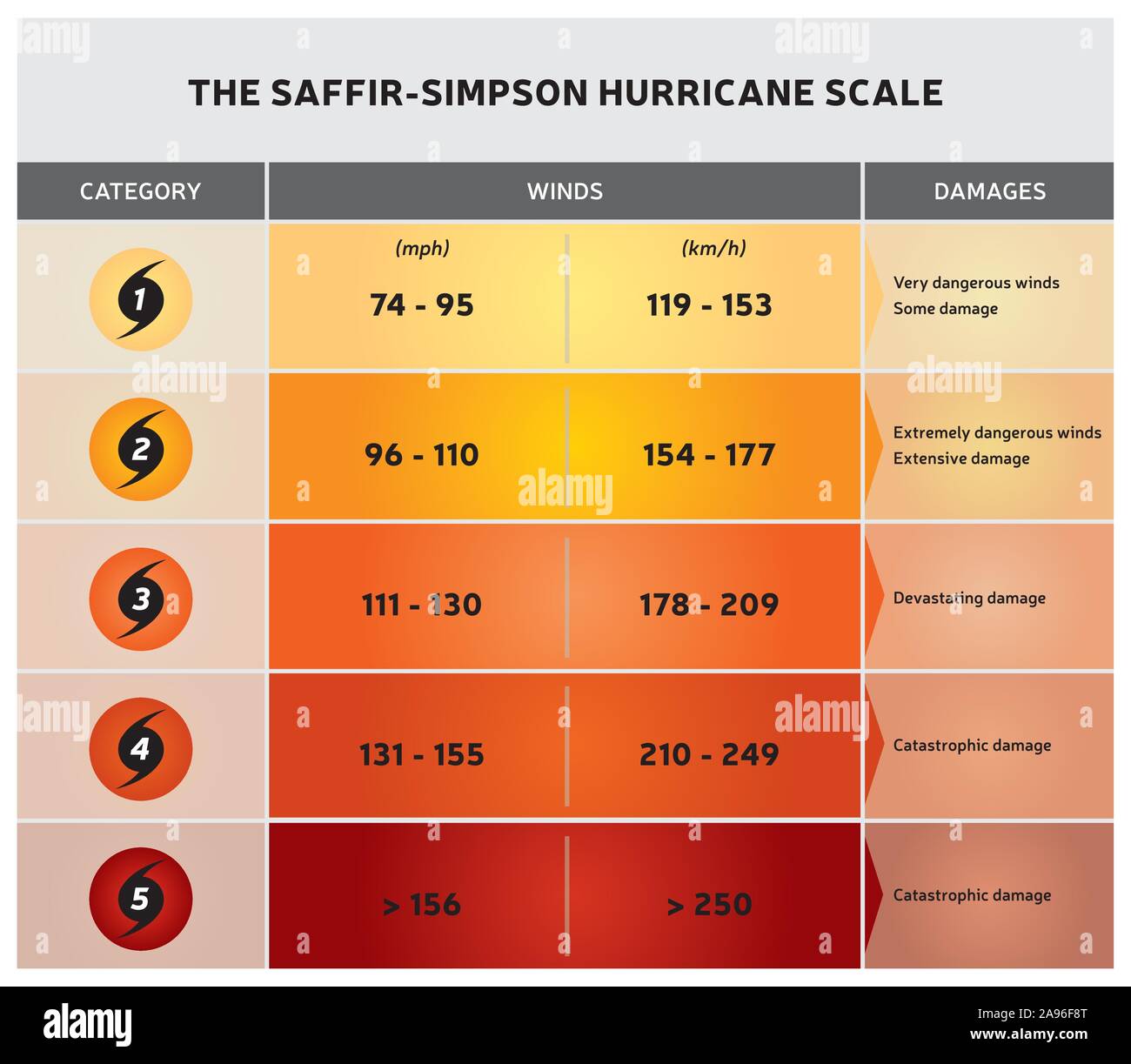
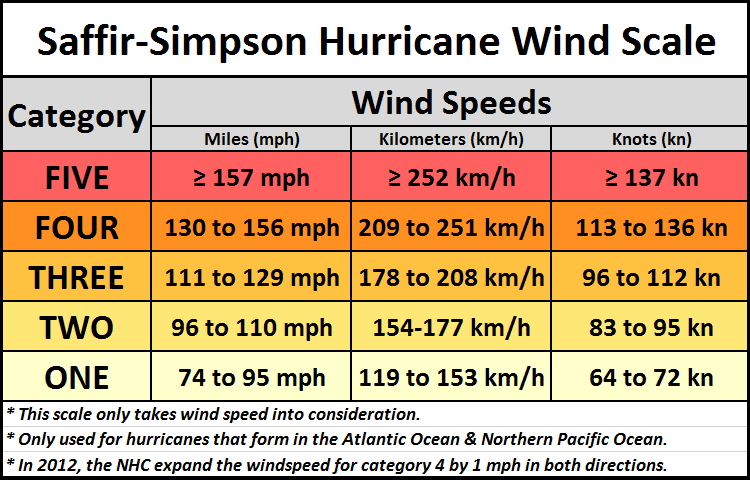
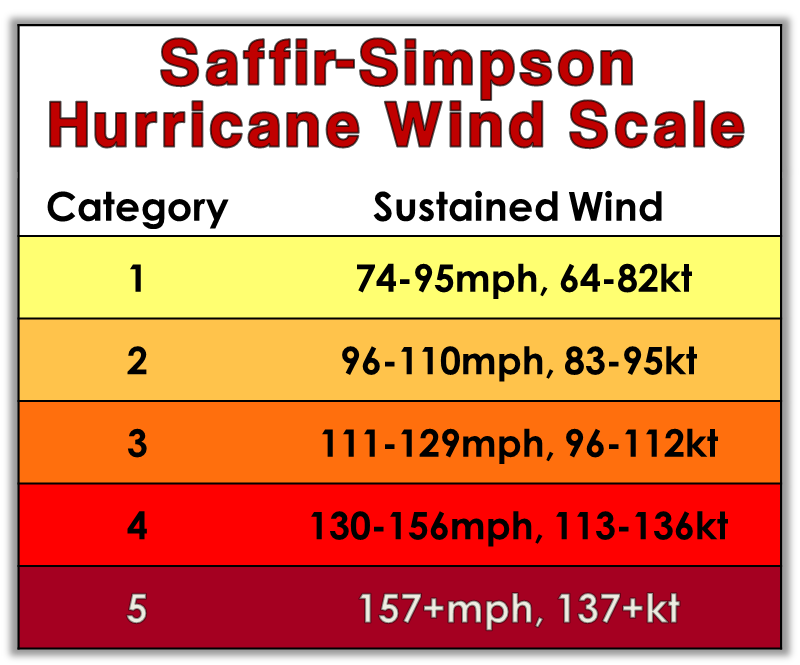
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale consists of five categories, each representing a range of sustained wind speeds and corresponding potential impacts. The categories are:
- Category 1 (74-95 mph): Minimal damage, with some tree branches broken and minor damage to roofs.
- Category 2 (96-110 mph): Moderate damage, with more extensive tree damage, roof damage, and potential coastal flooding.
- Category 3 (111-129 mph): Extensive damage, with widespread tree damage, major roof damage, and significant coastal flooding.
- Category 4 (130-156 mph): Catastrophic damage, with severe tree damage, significant structural damage to buildings, and extensive coastal flooding.
- Category 5 (157 mph or higher): Devastating damage, with widespread structural damage, complete roof failures, and catastrophic coastal flooding.
Beyond Wind Speed:
While the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale primarily focuses on wind speed, it is essential to understand that other factors contribute to the overall impact of a hurricane. These include:
- Storm Surge: This refers to the abnormal rise in sea level caused by a hurricane’s winds pushing water towards the shore. Storm surge can be highly destructive, causing flooding and erosion.
- Rainfall: Hurricanes can produce heavy rainfall, leading to flash flooding and landslides.
- Tornadoes: While less frequent, hurricanes can spawn tornadoes, further amplifying the damage potential.
The Importance of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale plays a crucial role in hurricane preparedness and response:
- Public Awareness: It provides a simple, understandable framework for communicating the severity of hurricanes to the public.
- Emergency Planning: Emergency managers use the scale to anticipate potential impacts and develop appropriate response plans.
- Infrastructure Design: The scale informs the design and construction of buildings and infrastructure to withstand hurricane-force winds.
- Insurance Assessment: Insurance companies use the scale to assess potential damage and determine coverage.
Understanding the Scale’s Limitations:
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a valuable tool, but it has limitations:
- Focus on Wind Speed: It primarily considers wind speed, neglecting other factors like storm surge and rainfall.
- Categorization: The categories provide a general assessment but don’t capture the nuances of individual hurricanes.
- Local Impact: The same hurricane category can have drastically different impacts depending on local geography and vulnerability.
Related Searches and FAQs:
1. Hurricane Categories:
-
What are the different hurricane categories?
- The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale classifies hurricanes into five categories based on their sustained wind speeds. Each category represents a range of wind speeds and associated damage potential.
-
What is the strongest hurricane category?
- Category 5 is the strongest hurricane category, with sustained wind speeds of 157 mph or higher.
-
What is the weakest hurricane category?
- Category 1 is the weakest hurricane category, with sustained wind speeds of 74-95 mph.
2. Hurricane Damage:
-
What kind of damage can a Category 5 hurricane cause?
- Category 5 hurricanes can cause devastating damage, including widespread structural damage, complete roof failures, and catastrophic coastal flooding.
-
What is the difference between wind damage and storm surge damage?
- Wind damage is caused by the hurricane’s strong winds, which can damage buildings, trees, and infrastructure. Storm surge damage is caused by the abnormal rise in sea level due to the hurricane’s winds pushing water towards the shore, leading to flooding and erosion.
-
How can I prepare for hurricane damage?
- It is crucial to have a hurricane preparedness plan that includes securing your home, stocking emergency supplies, and knowing evacuation routes.
3. Hurricane Tracking:
-
How are hurricanes tracked?
- Hurricanes are tracked using weather satellites, radar, and reconnaissance aircraft.
-
Where can I find the latest hurricane information?
- Reliable sources for hurricane information include the National Hurricane Center, local news outlets, and weather apps.
-
What is a hurricane watch and warning?
- A hurricane watch means that hurricane conditions are possible within a specified area, while a hurricane warning indicates that hurricane conditions are expected within a specified area.
4. Hurricane History:
-
What was the strongest hurricane ever recorded?
- The strongest hurricane ever recorded was Typhoon Tip in 1979, with sustained wind speeds of 190 mph.
-
What are some of the most devastating hurricanes in history?
- Some of the most devastating hurricanes in history include Hurricane Katrina (2005), Hurricane Andrew (1992), and Hurricane Harvey (2017).
-
How has the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale evolved over time?
- The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale has been revised several times since its inception, incorporating new knowledge and understanding of hurricane behavior.
5. Hurricane Forecasting:
-
How accurate are hurricane forecasts?
- Hurricane forecasts have become significantly more accurate over time due to advances in technology and understanding of hurricane dynamics.
-
What factors influence hurricane forecasts?
- Factors influencing hurricane forecasts include the hurricane’s current location, intensity, direction, and speed, as well as atmospheric conditions.
-
How often are hurricane forecasts updated?
- Hurricane forecasts are updated regularly, typically every few hours, to reflect the latest information and observations.
6. Hurricane Safety:
-
What are the best ways to stay safe during a hurricane?
- During a hurricane, it is essential to stay informed, follow official instructions, and seek shelter in a safe location.
-
What are some hurricane safety tips?
- Secure your home, gather emergency supplies, have a communication plan, and know your evacuation routes.
-
How can I help others during a hurricane?
- You can help others by volunteering, donating to relief organizations, and spreading awareness about hurricane preparedness.
7. Hurricane Climate Change:
-
How does climate change affect hurricanes?
- Climate change is expected to intensify hurricanes, leading to stronger wind speeds, higher storm surges, and increased rainfall.
-
What are the potential consequences of climate change on hurricane activity?
- Climate change could lead to more frequent and intense hurricanes, potentially causing greater damage and disruptions.
-
How can we mitigate the impacts of climate change on hurricanes?
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and investing in sustainable development are crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change on hurricanes.
8. Hurricane Research:
-
What are some ongoing research efforts related to hurricanes?
- Research efforts focus on improving hurricane forecasting, understanding the impacts of climate change on hurricanes, and developing strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
-
How is technology being used to improve hurricane research?
- Advanced weather satellites, radar systems, and computer modeling are being used to gather more data and improve hurricane forecasts.
-
What are the challenges and opportunities in hurricane research?
- Challenges include the complexity of hurricane dynamics and the need for more data, while opportunities lie in harnessing new technologies and collaborating across disciplines.
Tips for Hurricane Preparedness:
- Develop a Family Plan: Discuss evacuation routes, communication methods, and meeting points in case of separation.
- Prepare a Hurricane Kit: Include essential items like food, water, first-aid supplies, batteries, and a radio.
- Secure Your Home: Trim trees, board up windows, and bring loose objects inside to minimize wind damage.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and follow official instructions from local authorities.
- Know Your Evacuation Zone: Be familiar with evacuation routes and designated shelters in your area.
Conclusion:
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale provides a valuable framework for understanding and communicating the potential impact of hurricanes. However, it is crucial to recognize its limitations and consider the broader context of hurricane hazards. By understanding the scale, preparing for potential impacts, and staying informed, we can minimize risks and enhance our resilience to these powerful storms.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Hurricane Strength: A Comprehensive Guide to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
