Understanding the Significance of Power Outages: A Comprehensive Analysis
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of Power Outages: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of Power Outages: A Comprehensive Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of Power Outages: A Comprehensive Analysis
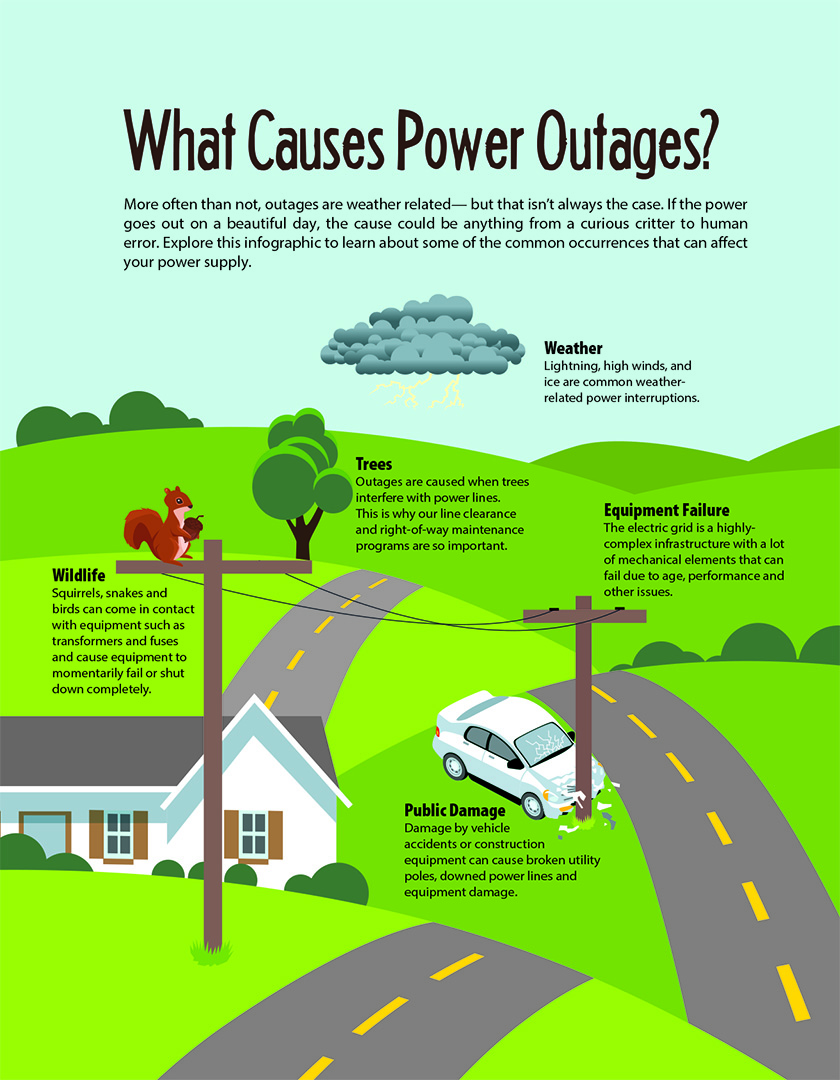
Power outages, a common occurrence in many parts of the world, can significantly disrupt daily life, impacting businesses, homes, and critical infrastructure. While the causes of these outages vary, understanding their impact and the strategies employed to mitigate their effects is crucial. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricacies of power outages, exploring their causes, consequences, and the vital role of FPL Report in addressing them.
The Multifaceted Causes of Power Outages
Power outages can arise from a multitude of factors, ranging from natural disasters to equipment malfunctions.
1. Natural Disasters:
- Severe Weather: Storms, hurricanes, tornadoes, and heavy snowfall can damage power lines, transformers, and other infrastructure, leading to widespread outages.
- Flooding: Rising water levels can inundate power stations and substations, causing electrical short circuits and equipment damage.
- Earthquakes: Seismic activity can trigger power outages by disrupting power lines, causing transformers to malfunction, or damaging power plants.
2. Equipment Malfunctions:
- Transformer Failures: Transformers are essential components in the power grid, and their failure can disrupt power flow to a specific area.
- Line Faults: Damage to power lines, often caused by aging infrastructure, weather conditions, or animal interference, can lead to outages.
- Power Plant Issues: Malfunctions in power plants, such as boiler failures or turbine problems, can significantly impact the power supply.
3. Human Error:
- Construction Accidents: Accidental damage to power lines during construction projects can result in outages.
- Maintenance Neglect: Lack of regular maintenance can lead to equipment failure, causing outages.
- Cyberattacks: Intentional disruption of power grids through cyberattacks can lead to widespread outages.
4. Other Factors:
- Demand Overload: Excessively high demand for electricity can strain the power grid, leading to outages.
- Planned Outages: Scheduled power outages for maintenance or repairs can also affect power supply.
The Consequences of Power Outages
Power outages can have a wide range of consequences, impacting various aspects of society:
1. Economic Impact:
- Business Disruptions: Outages can halt production, disrupt operations, and lead to financial losses for businesses.
- Loss of Productivity: Workers may be unable to perform their duties, leading to reduced productivity.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Outages can disrupt supply chains, affecting the availability of goods and services.
2. Public Safety:
- Traffic Signals: Outages can cause traffic disruptions, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Medical Facilities: Hospitals and other medical facilities rely heavily on electricity, and outages can compromise patient care.
- Emergency Services: Outages can hamper the ability of emergency services to respond effectively to incidents.
3. Social Impact:
- Communication Disruptions: Outages can disrupt phone, internet, and television services, impacting communication and access to information.
- Food Spoilage: Outages can lead to food spoilage in refrigerators and freezers, causing financial losses and potential health risks.
- Discomfort and Inconvenience: Outages can cause discomfort and inconvenience for residents, especially during extreme weather conditions.
The Crucial Role of FPL Report
FPL Report is an essential tool for managing power outages and ensuring a reliable power supply. This comprehensive reporting system provides real-time information on power outages, enabling utilities to:
- Identify the Cause of Outages: FPL Report helps pinpoint the source of outages, allowing for targeted troubleshooting and faster restoration of power.
- Track Outage Progress: The system provides updates on the number of customers affected, the estimated time of restoration, and the progress of repair efforts.
- Communicate with Customers: FPL Report facilitates communication with customers, providing them with timely updates and information about the outage.
- Improve System Reliability: By analyzing outage data, utilities can identify patterns and trends, enabling them to implement measures to improve system reliability and prevent future outages.
Exploring Related Searches
Understanding the nuances of power outages necessitates exploring related search terms that provide deeper insights into this complex issue.
1. Power Outage Statistics:
- Global Power Outage Data: Analyzing global statistics reveals the frequency and duration of power outages in different regions.
- Outage Trends: Identifying trends in outage frequency and duration helps understand the evolving dynamics of power systems.
- Economic Costs of Outages: Quantifying the financial impact of outages on businesses and economies provides a clearer picture of their overall cost.
2. Power Outage Prevention:
- Grid Modernization: Investing in grid modernization projects, such as smart grids and advanced technologies, can enhance system resilience and prevent outages.
- Tree Trimming: Regular tree trimming around power lines reduces the risk of tree branches falling and causing outages.
- Undergrounding Power Lines: Burying power lines underground protects them from severe weather and other environmental factors.
3. Power Outage Response:
- Emergency Response Plans: Utilities develop comprehensive emergency response plans to ensure a coordinated and efficient response to power outages.
- Outage Restoration Techniques: Exploring various techniques for restoring power, such as using mobile generators and temporary power lines, enhances the efficiency of outage response.
- Customer Communication Strategies: Effective communication strategies ensure that customers are informed about outages and the progress of restoration efforts.
4. Power Outage Technology:
- Smart Grid Technologies: Smart grid technologies enable real-time monitoring of the power grid, facilitating early detection and prevention of outages.
- Distributed Generation: Utilizing distributed generation sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can enhance system resilience and reduce dependence on centralized power plants.
- Battery Storage: Implementing battery storage systems can provide backup power during outages, ensuring continuous power supply to critical infrastructure.
5. Power Outage Safety:
- Safety Precautions During Outages: Understanding safety precautions, such as avoiding contact with downed power lines and using flashlights instead of candles, minimizes the risk of accidents during outages.
- Generator Safety: Proper installation and operation of generators ensure safe and efficient power supply during outages.
- Carbon Monoxide Awareness: Educating the public about the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning from generators and other sources is crucial during outages.
6. Power Outage Impacts on Businesses:
- Business Continuity Planning: Businesses develop business continuity plans to minimize the impact of outages on their operations.
- Backup Power Systems: Implementing backup power systems, such as generators or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), ensures continuous operation during outages.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly backing up data and having a robust data recovery plan is essential for businesses to avoid data loss during outages.
7. Power Outage Impacts on Critical Infrastructure:
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals rely on electricity for critical medical equipment and patient care, requiring backup power systems and emergency response plans.
- Water Treatment Plants: Outages can disrupt water treatment processes, impacting water quality and availability.
- Transportation Systems: Outages can disrupt transportation systems, including airports, railways, and traffic signals, leading to widespread disruptions.
8. Power Outage Impacts on the Environment:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Outages can lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions from backup generators and power plants.
- Environmental Damage: Outages can impact sensitive ecosystems, such as wildlife habitats, through disruptions to power supply and increased pollution.
- Sustainable Energy Solutions: Promoting renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures can mitigate the environmental impact of power outages.
FAQs on FPL Report
1. What is the purpose of FPL Report?
FPL Report is a comprehensive reporting system that provides real-time information on power outages, enabling utilities to manage outages effectively, identify the causes, track progress, and communicate with customers.
2. How does FPL Report benefit customers?
FPL Report benefits customers by providing timely updates on outages, estimated restoration times, and communication channels for inquiries. This transparency enhances customer satisfaction and reduces anxiety during outages.
3. How does FPL Report improve system reliability?
FPL Report helps utilities analyze outage data, identify patterns and trends, and implement measures to improve system reliability, preventing future outages.
4. Is FPL Report available to all utilities?
While FPL Report is a widely used system, its availability may vary depending on the utility provider. Contact your local utility for information on their reporting system.
5. What information is included in FPL Report?
FPL Report typically includes information such as the number of customers affected, the location and cause of the outage, the estimated time of restoration, and updates on the progress of repair efforts.
Tips for Managing Power Outages
- Prepare a Family Emergency Plan: Develop a plan that includes communication strategies, evacuation routes, and essential supplies for each family member.
- Keep a Battery-Powered Radio and Flashlights: Ensure you have reliable sources of light and information during outages.
- Charge Electronics: Charge your phones, laptops, and other devices before an outage to ensure you have access to communication and essential tools.
- Check on Neighbors: Check on elderly neighbors or those with special needs to ensure their safety during outages.
- Use Generators Safely: If using a generator, ensure proper ventilation and follow safety guidelines to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Be Patient: Outages can be frustrating, but it’s important to be patient and cooperate with utility crews working to restore power.
Conclusion
Power outages are a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While they can be caused by a variety of factors, understanding their impact and the role of FPL Report in managing them is crucial. By investing in grid modernization, implementing effective response strategies, and promoting responsible energy consumption, we can strive to minimize the impact of power outages and ensure a reliable and sustainable power supply for the future.
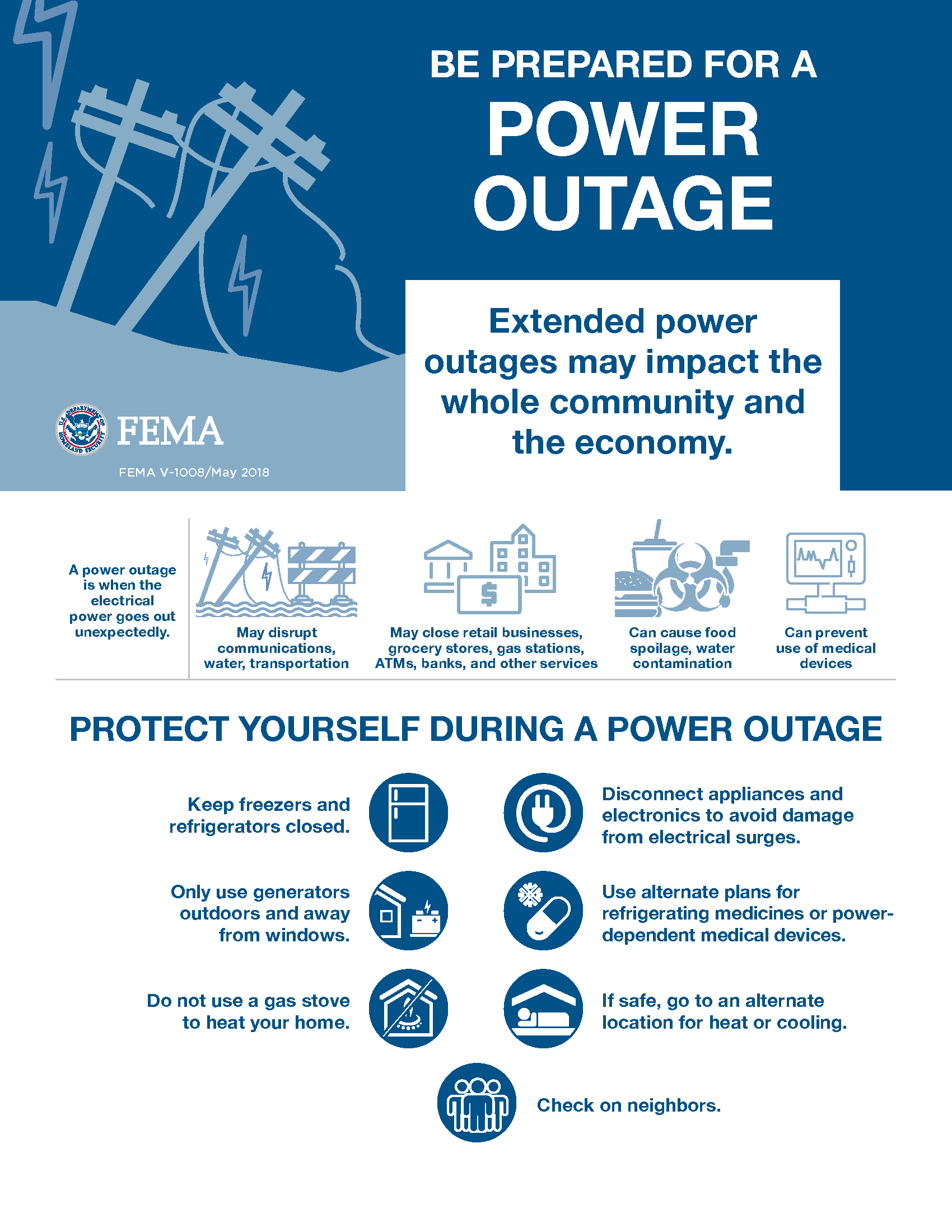







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of Power Outages: A Comprehensive Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
